Swing Trading Strategies and Techniques for Every Trader
Swing trading strategies offer traders the opportunity to capitalize on short- to medium-term price movements by holding positions for several days to weeks. By analyzing market trends and identifying key support and resistance levels, swing traders aim to enter trades at optimal points and ride the momentum for maximum profit. CScalp explores this approach.
Attention! This article is for informational purposes only and does not contain recommendations or calls to action.
The review has been prepared by the CScalp terminal team. You can get CScalp by leaving your e-mail in the form below.

Swing Trading Basics
Swing trading is a type of trading that involves holding positions for several days to several weeks. In swing trading, traders work with price “swings” that unfold over a few days or weeks. These are often corrections within larger global trends. The highest points of such corrections are called swing highs, while the lowest points are called swing lows.
To take full advantage of swing trading strategies, try the professional trading platform CScalp by leaving your email in the form above. With the free terminal, you will be able to connect to your preferred exchange and place orders with one click, as well as automatically manage your risks.
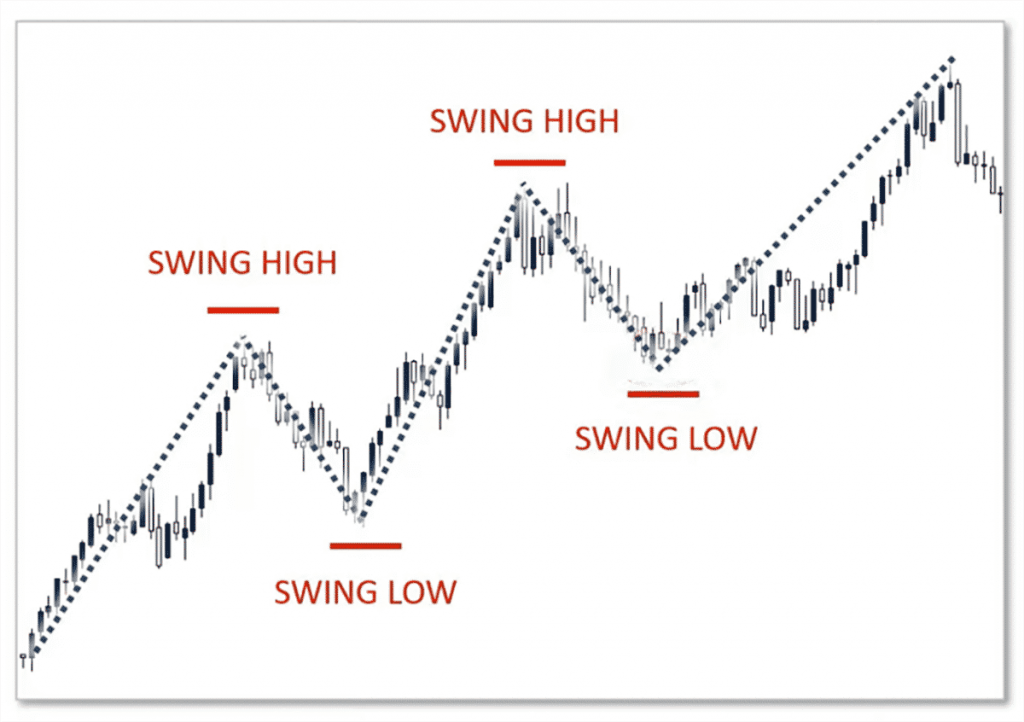
Corrections serve as a “pivot point” for fixing, opening, and closing positions. Depending on the strategy, at each “swing,” a trader can add to a position, close it partially or completely, or open a hedge in the opposite direction, etc. A typical swing trader aims to “squeeze” the maximum out of every global trend. Key decisions are made during swings/corrections.
Swing traders typically do not operate in sideways markets. The reason is that sideways markets offer less profit potential over medium distances. More control over the position is needed than in a trending market. For decision-making, swing traders need unambiguous price maneuvers – breakouts, bounces, and corrections. For them, sideways markets are a “gray area,” a period of waiting.
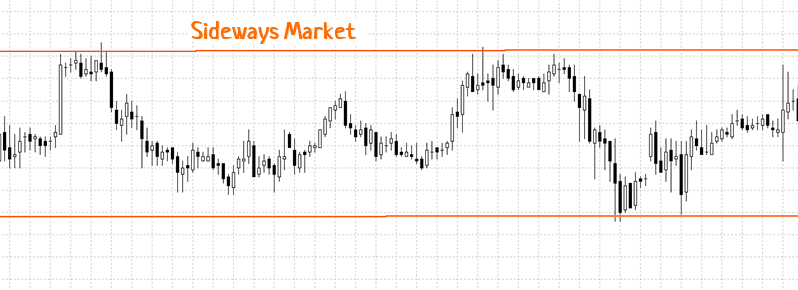
If a swing trader wants to trade in a sideways market, they use grid (channel) bots, which automatically buy and sell assets within specified price ranges.
Key Terms of Swing Trading
Swing traders primarily rely on technical analysis. To find entry and exit points, they study price charts and technical indicator readings. The main working time frames are daily and weekly. Specific entry points are usually sought on the 4-hour (4H) or 1-hour (1H) time frames.
Candlestick and chart pattern analysis plays a significant role in swing trading. On higher time frames (4H, 1D, 1W), patterns and indicators carry more “weight.” A lot of activity occurs in these time frames, and price movements on them “live” long enough to be confirmed. Candlestick patterns such as the Doji or Engulfing are also relevant on these time frames (discussed below).
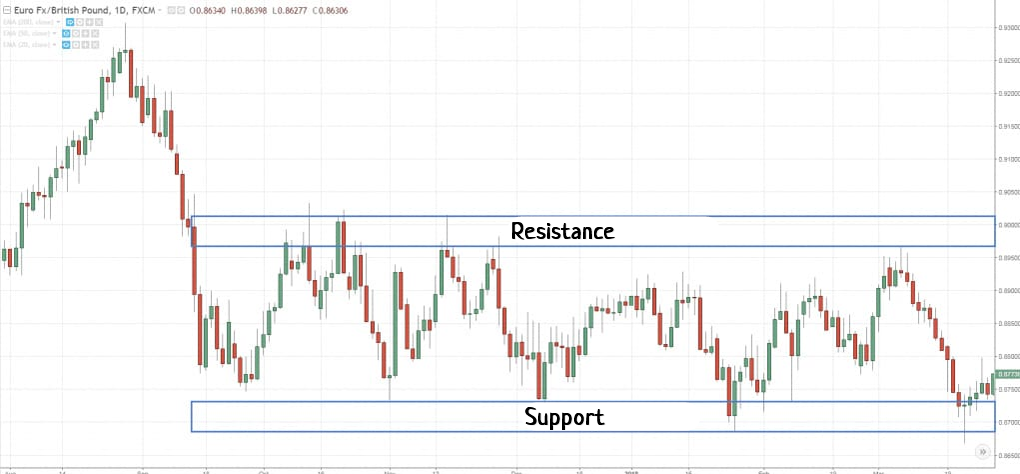
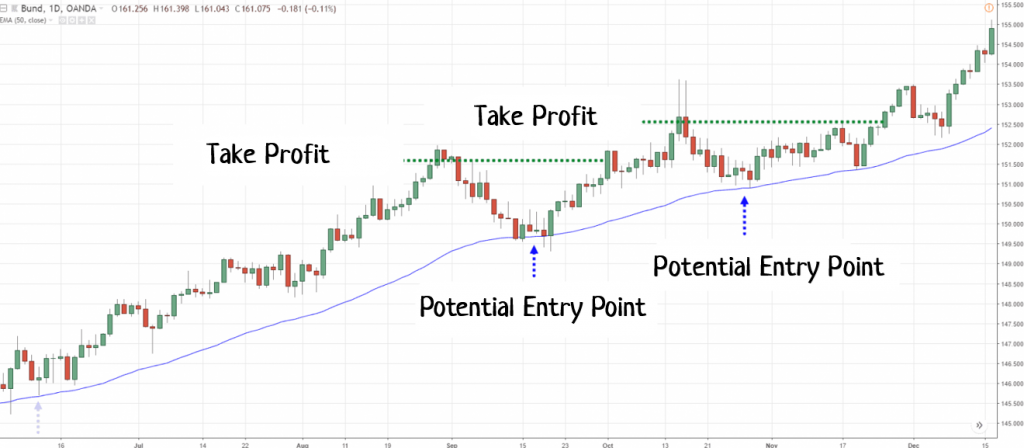
In swing trading, the analysis of support and resistance levels – both global and local – is important. Levels are areas where the price reacts by either bouncing off or breaking through them. Trading decisions in swing trading are based on these reactions – buying or selling at the level. On higher time frames, levels are particularly relevant because all market participants see them, which means they “believe” in them.

Comparison with Other Trading Styles
Swing trading differs from day trading and long-term investing, offering unique benefits and challenges.
- Swing Trading vs. Day Trading: Day trading involves buying and selling within the same day, requiring constant market monitoring and rapid decisions. It suits traders who can dedicate full attention to the markets but incur higher transaction costs due to frequent trades. Swing trading, on the other hand, involves holding positions for several days to weeks, capturing broader price swings with less time commitment and lower costs.
- Swing Trading vs. Long-Term Investing: Long-term investing focuses on holding assets for years, benefiting from gradual appreciation and relying on fundamental analysis. It offers lower risk through time diversification. Swing trading seeks short- to medium-term gains using technical analysis, requiring more active management and precise timing but potentially offering higher returns.
Tools and Indicators for Swing Trading
Swing trading relies on a variety of tools and indicators to identify profitable trading opportunities and make informed decisions. These tools help traders analyze market trends, determine entry and exit points, and manage risk effectively.
Technical Indicators
Moving averages (MA) are used to determine the direction and strength of a trend. The main “signal” in swing trading is: that if the price moves above the moving average, it indicates a bullish trend; if it moves below, it indicates a bearish trend.
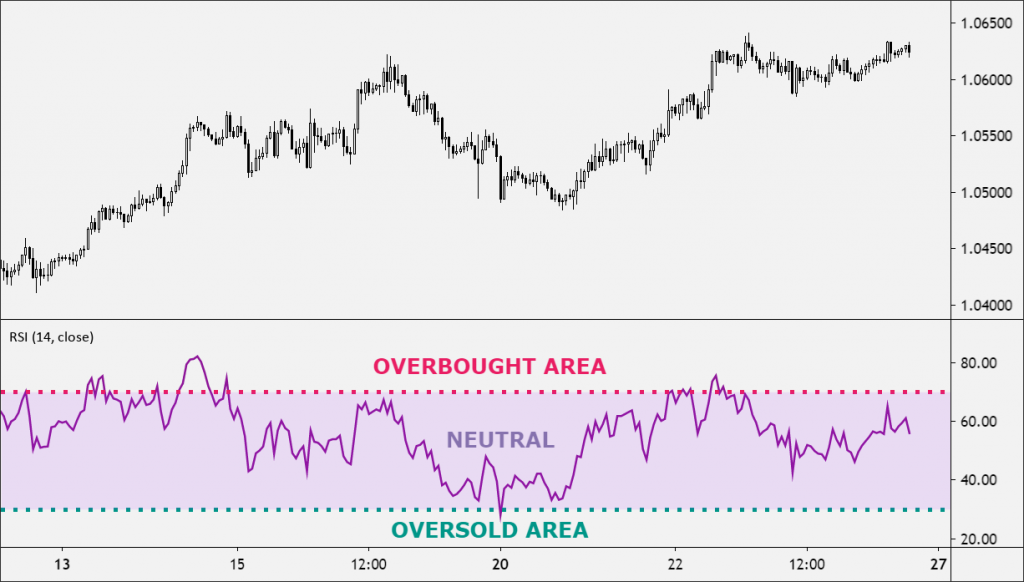
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) measures the “strength” of an asset’s price. A high RSI reading (70+) indicates that the asset is overbought, while a low RSI reading (30-) indicates that it is oversold. Typically, assets are sold at overbought levels and bought at oversold levels.
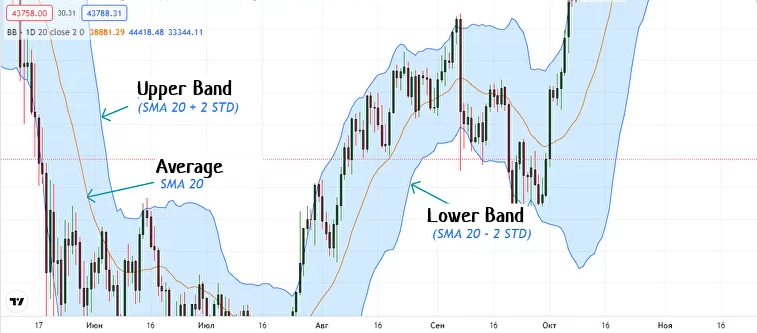
Bollinger Bands are used to measure the volatility of an instrument. The lines are plotted at two standard deviations from the moving average. When the price approaches the upper band, it indicates an overbought market. When the price is closer to the lower band, it means an oversold market. Crossings of price trends and other movements with the bands are also observed. Key trend reversals can occur at these intersections.
The Fibonacci Retracement tool helps identify potential support and resistance levels. It is based on the idea that an asset’s price moves in predictable sections that can be measured using Fibonacci ratios. Corrections and reversals often occur at key points of these ratios (in theory).
MACD is used to identify price momentum. In swing trading, traders look for crossovers. When the MACD line crosses above the signal line, it is a bullish signal, and when it crosses below, it is a bearish signal.
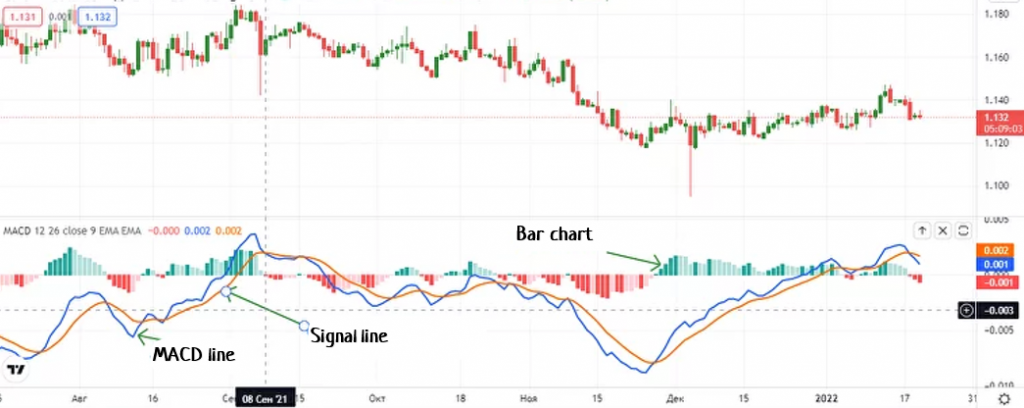
Chart Patterns in Swing Trading
Swing traders use chart patterns to identify potential entry and exit points. Here, we will review some patterns.
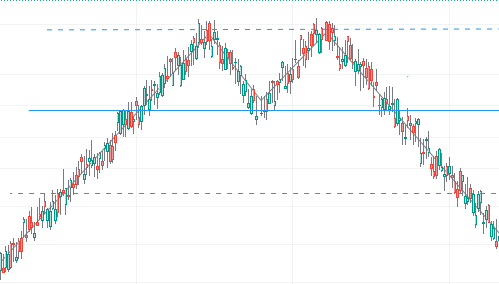
The Double Top/Double Bottom pattern occurs when the price reaches a high or low point, retraces, and then returns to the same high or low point before reversing the trend. Swing traders sell from the “top” and buy from the “bottom.” These points on higher time frames indicate a strong level of support or resistance.
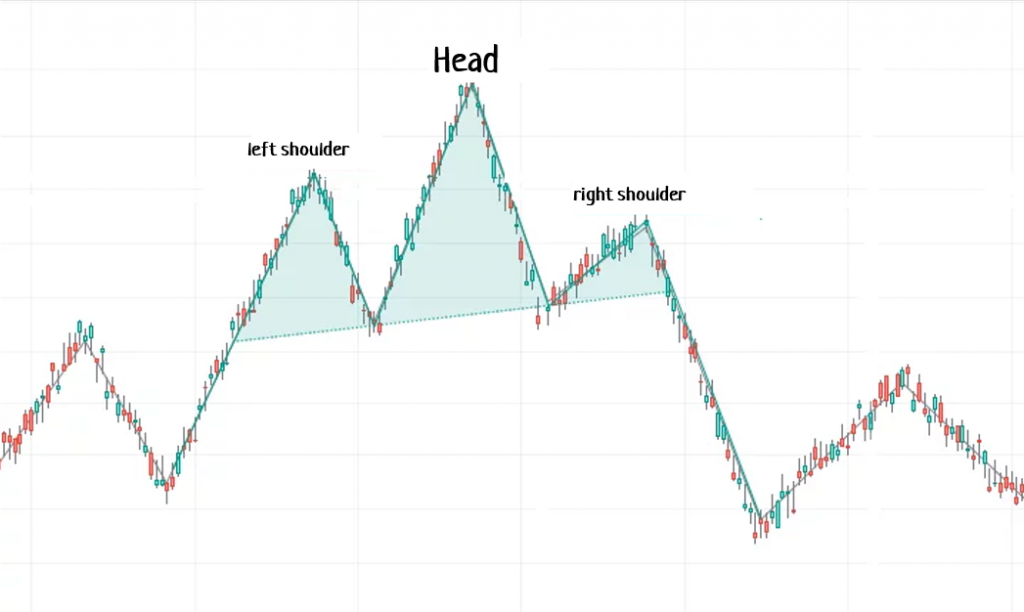
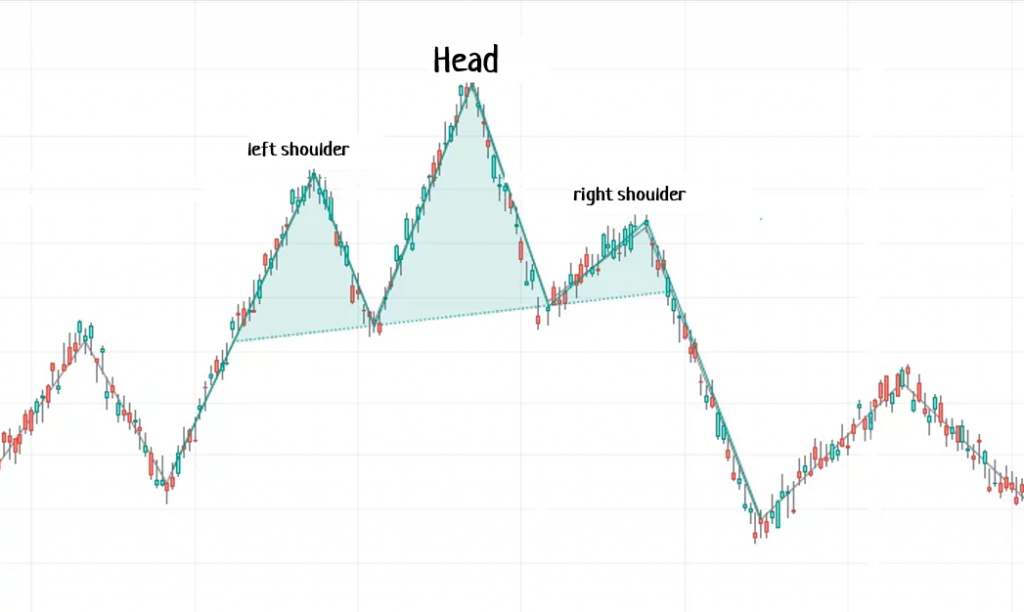
The “Head and Shoulders” pattern forms when the price reaches a high point, retraces, then reaches a higher high, retraces, and finally reaches a lower high. This looks like a peak surrounded by two lower peaks. Swing traders use this pattern to identify potential trend reversals. If the “neckline” is broken, it is considered a signal to sell.
Bullish and bearish flags are used as trend continuation signals. The pattern consists of a sharp, strong price movement followed by a period of sloped consolidation in the opposite direction. During the consolidation phase, the price moves within a narrow range, forming a rectangular shape resembling a flag. When the price breaks out of the rectangle, it usually continues in the direction of the previous trend. Swing traders can use “flags” as entry and exit points as well as stop-loss levels.
The Cup and Handle pattern is used to identify potential breakouts to the upside. The pattern forms when the price of an asset falls and then rises again, creating a “U” shape (the cup). After the rise, there is another small U-shaped dip (the handle). The handle should be relatively flat and not retreat much from the cup. Swing traders look for a breakout above the handle’s resistance level as confirmation of a potential bullish move. A volume indicator can be used to confirm the pattern. After the “breakout,” swing traders open a long position and place stop-losses slightly below the level.
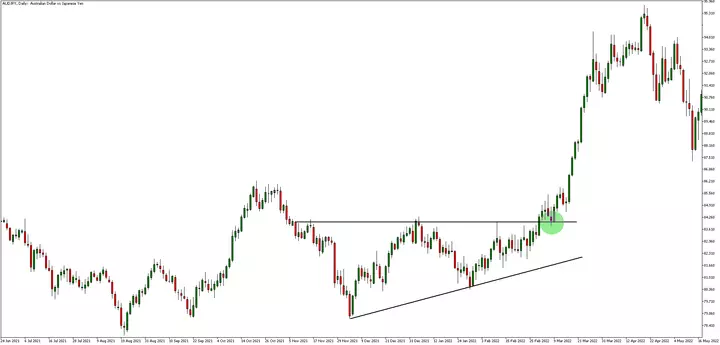
Triangles are used to identify potential breakouts. The pattern is formed by two trendlines converging at a single point. These trendlines form a triangle shape. There are symmetrical and ascending/descending triangles.
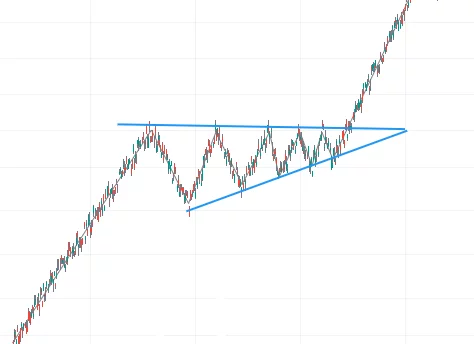
Swing traders look for a breakout of the triangle pattern, which can indicate a potential continuation or reversal of the trend. A breakout occurs when the price moves above or below one of the trendlines. Indicators are used for confirmation, such as volume and moving averages.
Candlestick Patterns in Swing Trading
Candlestick patterns are popular in swing trading as they help identify potential trend reversals or continuations. These patterns are more relevant for swing trading than for day trading or scalping because, on higher time frames (4H/1D+), each candle contains more information, making the candlestick patterns more valid.
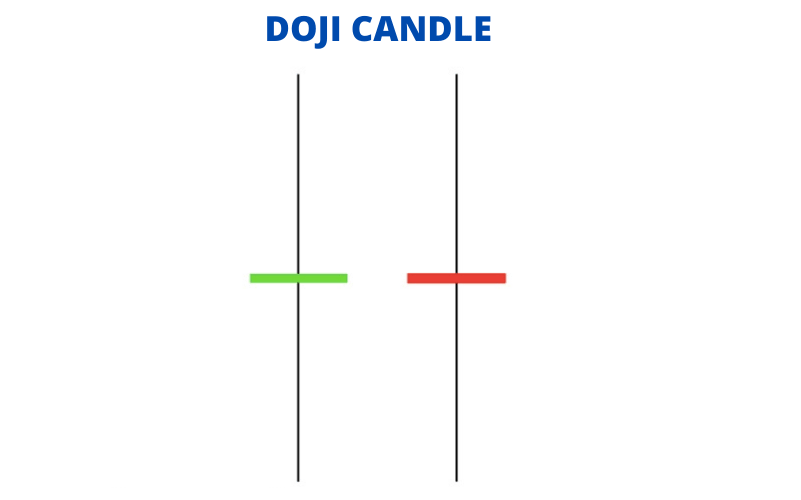
A Doji occurs when the opening and closing prices of an asset are nearly equal. This indicates indecision in the market and a potential trend reversal.
A Hammer has a long lower shadow and a short upper shadow. This indicates that buyers took control after a period of selling, suggesting a likely upward movement. An Inverted Hammer is a reverse scenario, indicating a potential downward movement. This pattern precedes a move to short.
A Shooting Star is characterized by a long upper shadow and a short lower shadow. This indicates the dominance of sellers and a likely move downward.
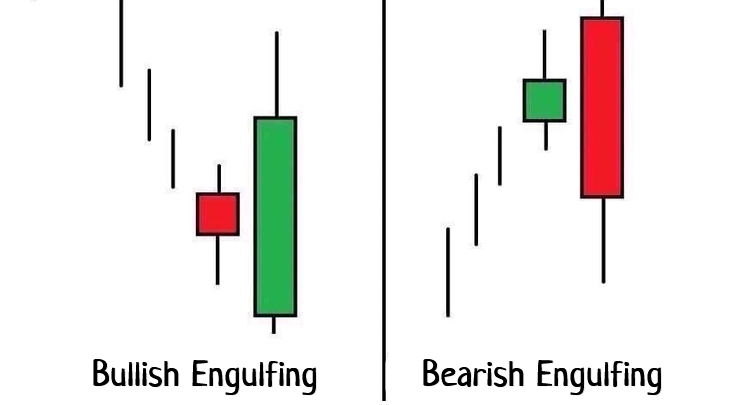
An Engulfing pattern occurs when a small candle is followed by a larger candle in the opposite direction. This indicates a probable trend reversal.
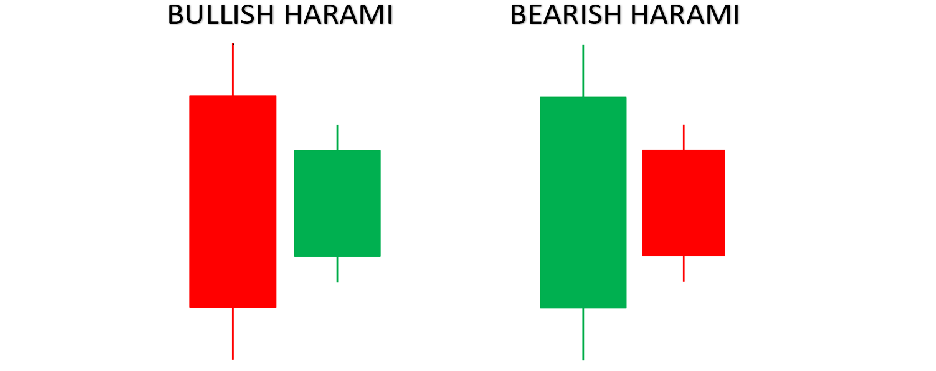
A Harami occurs when a small candle is followed by a larger candle within the same price range (the opposite of an “engulfing” pattern). This indicates indecision in the market and a potential trend reversal.
Key Strategies: Breakout Swing Trading Strategy, Moving Average and Others
Swing trading strategies vary based on individual preferences. Some traders hold positions for a week, while others may extend to a month. Swing trading requires flexibility and adaptability. Successful swing traders know when to enter and exit trades.
Fibonacci Retracement
Fibonacci retracement serves as a powerful tool in swing trading. Traders use this strategy to identify potential entry points. The Fibonacci levels act as support and resistance zones. These levels help traders predict price movements. In a strong uptrend, a stock’s price may pull back to a key Fibonacci level. The price often bounces off this support zone. This confirms the validity of the retracement trade.
As the uptrend resumes, traders may scale out of their positions. Trailing stop-loss orders secure profits and protect against reversals. Fibonacci retracement remains a staple among swing trading strategies.
Trend Trading
Trend trading focuses on identifying and following market trends. Traders aim to capitalize on the momentum of a stock. This strategy works well in both uptrends and downtrends. Traders use technical analysis tools to confirm trends.
Moving averages often serve as key indicators. A rising moving average signals an uptrend. A falling moving average indicates a downtrend. Traders enter positions in the direction of the trend. Exiting positions occur when the trend shows signs of reversal. Trend trading requires patience and discipline. This strategy offers consistent returns for diligent traders.
Reversal Trading
Reversal trading targets significant changes in market direction. Traders look for signs that a current trend is losing momentum. Technical indicators like RSI and MACD help identify reversals. Overbought or oversold conditions often signal potential reversals. Traders enter positions opposite to the prevailing trend. This strategy aims to catch the wave of a new trend.
Breakout Strategy
Breakout trading focuses on identifying key price levels where a stock’s price breaks through resistance or support. Traders use this strategy to capitalize on significant price movements. Breakout trading involves entering a trade when the stock price moves beyond a defined level. This strategy aims to catch strong price momentum. Breakout traders often use technical analysis tools to identify potential breakout points. Charts and indicators help traders spot these critical levels. A successful breakout trade can lead to substantial profits.
Risk management remains crucial in breakout trading. Traders must set stop-loss orders to protect against false breakouts. Breakout trading offers opportunities for quick gains.
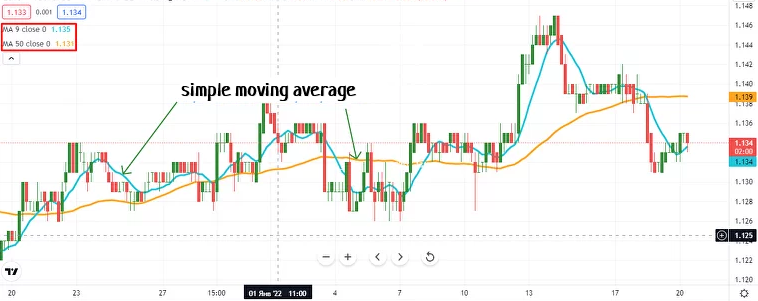
Simple Moving Averages
Simple moving averages (SMA) serve as a fundamental tool in swing trading. Traders use SMAs to identify trends and potential entry points. An SMA calculates the average price of a stock over a specified period. This average helps smooth out price fluctuations. Traders often use the 50-day and 200-day SMAs. A rising SMA indicates an uptrend. A falling SMA signals a downtrend. Traders enter positions based on the direction of the SMA.
Exiting positions occurs when the trend shows signs of reversal. SMAs provide a clear visual representation of price trends. This strategy offers a straightforward approach to swing trading. Successful traders rely on SMAs for consistent results.
Risk Management in Swing Trading
Risk management is a fundamental aspect of swing trading, ensuring that traders can confidently navigate the market and protect their capital from adverse price movements. By implementing effective risk management strategies, traders can minimize losses and enhance their long-term profitability.
Importance of Risk Management
Risk management stands as a cornerstone in swing trading, providing a framework for traders to navigate volatile markets and preserve their capital. It involves a series of practices that help traders minimize potential losses while maximizing potential gains.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Setting stop-loss orders is a fundamental aspect of risk management. These orders automatically close a trade when the price reaches a predetermined level, limiting potential losses.
- Position Sizing: Traders should never risk more than a small percentage of their capital on a single trade, typically between 1% and 3%. This approach ensures that no single trade can drastically impact the overall trading account, allowing traders to withstand losing streaks and maintain their long-term profitability.
- Diversification: By spreading investments across different assets or markets, traders can reduce the impact of any one position on their overall portfolio. Diversification helps mitigate risk and increases the likelihood of capturing profitable trades in different market conditions.
- Consistency and Discipline: Consistent application of risk management strategies enhances long-term profitability. Traders must remain disciplined and adhere to their risk management plans, avoiding impulsive decisions driven by emotions. Emotional decision-making often leads to significant losses, highlighting the importance of sticking to a well-structured risk management plan that provides peace of mind.
- Emotional Control: Maintaining emotional control is vital in swing trading, where market fluctuations can trigger fear and greed. A robust risk management plan helps traders maintain objectivity, reducing the likelihood of making rash decisions based on short-term market movements.
Skills Required for Successful Swing Trading
Successful swing trading requires a blend of skills and knowledge that enable traders to analyze markets effectively and make informed decisions.
- Analytical Abilities: Strong analytical abilities are essential for interpreting market data and identifying trading opportunities. Traders need to be adept at using technical analysis tools to evaluate chart patterns and indicators.
- Technical Analysis Proficiency: Technical analysis forms the backbone of swing trading strategies. Understanding chart patterns and indicators, such as moving averages and the Relative Strength Index (RSI), is crucial for identifying trends and potential entry and exit points.
- Market Awareness: Traders need to stay updated with market news and events that can impact price movements. Keeping abreast of economic data releases and geopolitical developments helps traders anticipate market shifts and adjust their strategies accordingly.
- Continuous Education: Enhances trading proficiency. Traders should seek out resources and training opportunities to improve their skills and stay current with market developments.
- Patience and Discipline: Patience and discipline are vital traits for swing traders, enabling them to wait for optimal trading setups and stick to their strategies. Traders must avoid impulsive decisions and remain committed to their trading plans.
- Adaptability: Allows traders to adjust to changing market conditions and refine their strategies as needed. The ability to adapt ensures traders can navigate different market environments and capitalize on new opportunities.
- Networking and Communication: Effective communication skills help in networking with other traders and learning from their experiences. Engaging with a community of traders can provide valuable insights and support.
- Commitment to Learning: A commitment to ongoing learning ensures continuous improvement in trading skills. Successful traders prioritize knowledge acquisition and seek out ways to enhance their understanding of market dynamics.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Swing trading, while offering profit opportunities, also presents several common pitfalls that can lead to significant losses if not carefully managed. Understanding these pitfalls and implementing strategies to avoid them is crucial for long-term success in trading.
Overtrading
Overtrading is a frequent pitfall for many traders, driven by the desire to be constantly active in the market. This urge can lead traders to make impulsive decisions without thorough analysis, ultimately resulting in significant financial losses. Swing trading requires patience and discipline to succeed. It is essential to wait for well-defined trading setups that align with your strategy rather than entering trades on a whim. Traders should focus on quality over quantity, prioritizing trades that have a higher probability of success.
Allowing market conditions, rather than emotions, to dictate when to trade is crucial in avoiding overtrading. Emotional trading often leads to overtrading and can quickly deplete your capital. Traders must adhere to their predefined trading plans and avoid letting impatience or greed influence their decisions. Consistent application of a trading strategy ensures long-term success, as a well-defined trading plan outlines specific criteria for entering and exiting trades, helping traders stay disciplined and focused on their goals. Setting realistic trading goals based on risk tolerance and market conditions can also help traders avoid the temptation to chase every potential trade, which can lead to overtrading and increased risk exposure.
Ignoring Risk Management
Always setting stop-loss orders for every trade helps limit potential losses during adverse market conditions, acting as a safeguard by automatically closing trades when prices move against your position. Position sizing is another crucial component in managing risk effectively. Traders should never risk more than a small percentage of their capital on a single trade, typically between 1% and 3%, minimizing the impact of any one trade on the overall account balance.
Diversification also plays an important role in spreading risk across different assets, which reduces the impact of a poor-performing trade. By investing in a variety of instruments, traders can mitigate the risk associated with market volatility and enhance their potential for returns.
To learn more about swing trading, check out our article “Learning Swing Trading for Beginners.”
Developing a Swing Trading Strategy
Creating a successful swing trading strategy involves careful planning and ongoing refinement. By establishing a clear trading plan and continuously testing and adjusting your approach, you can increase your chances of success in capturing profitable market swings.
Creating a Trading Plan
A well-defined trading plan is essential for successful swing trading. It serves as a roadmap for your trading activities and helps maintain discipline and consistency in your approach.
One of the key components of a trading plan is defining precise entry and exit criteria:
- Entry Criteria: Identify conditions that signal potential buying opportunities, such as a price bounce off a support level or a bullish crossover of moving averages. Clear entry criteria help ensure that you only enter trades that align with your strategy.
- Exit Criteria: Define conditions for closing a trade, such as reaching a predetermined profit target, hitting a stop-loss level, or observing signs of trend reversal. Establishing exit criteria helps protect profits and limit losses, enabling you to manage trades effectively.
Setting realistic goals and risk-reward ratios is crucial for maintaining a balanced approach to trading:
- Realistic Goals: Establish achievable trading goals based on your risk tolerance, trading style, and market conditions. Avoid setting overly ambitious targets that may lead to taking excessive risks.
- Risk-Reward Ratios: Determine your risk-reward ratio for each trade to ensure potential profits outweigh potential losses. A common practice is to aim for a risk-reward ratio of at least 1:2, meaning you stand to gain twice as much as you risk. This approach helps maintain profitability even with a lower win rate.
Backtesting and Strategy Refinement
Backtesting is a critical step in developing and refining a swing trading strategy. It involves testing your strategy on historical market data to evaluate its effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
Backtesting allows you to assess how your strategy would have performed in past market conditions without risking actual capital.
- Performance Evaluation: By simulating trades based on historical data, you can measure the strategy’s performance in terms of profitability, drawdowns, and consistency. This analysis helps identify strengths and weaknesses in your approach.
- Risk Management Assessment: Backtesting provides insights into how well your risk management techniques hold up under various market scenarios. You can evaluate whether your stop-loss levels and position sizes are appropriate for maintaining capital protection.
Once you have backtested your strategy, it’s essential to analyze the results and make necessary adjustments to enhance performance.
- Identifying Patterns: Look for recurring patterns in the data that indicate potential improvements or areas where the strategy may not perform well. This analysis can reveal insights into market behavior and help refine your approach.
- Strategy Refinement: Based on your analysis, make adjustments to your strategy to optimize entry and exit criteria, risk management, and other parameters. Continuously refine your approach to adapt to changing market conditions and improve overall performance.
- Ongoing Evaluation: Regularly monitor your strategy’s performance and make adjustments as needed. Market conditions and trading dynamics evolve, so staying flexible and responsive is key to maintaining a successful trading strategy.
Swing Trading Strategies – Conclusion
Swing trading strategies offer numerous opportunities for traders. Education remains crucial for mastering these strategies. Traders must understand the fundamentals of swing trading. Knowledge of technical analysis tools enhances trading success. Continuous education helps traders stay updated with market trends.
Effective swing trading strategies require discipline and patience. Traders must follow their trading plans consistently. Emotional decision-making often leads to losses. Successful traders rely on well-defined strategies. Risk management plays a vital role in protecting capital. Setting stop-loss orders minimizes potential losses. Position sizing ensures that traders do not risk too much on a single trade.
Swing trading strategies include various approaches. Fibonacci retracement helps identify potential entry points. Trend trading focuses on following market momentum. Reversal trading aims to catch new trends. Breakout strategy capitalizes on significant price movements. Simple moving averages provide clear trend signals. Each strategy requires a thorough understanding of market dynamics.
To further enrich your experience, we invite you to join our Discord server. Your insights, questions, and discussions will be a valuable addition to our growing community of traders.
Frequently Asked Questions: FAQs About Swing Trading Strategies
What Are Swing Trading Strategies and How Do They Differ From Day Trading?
Swing trading strategies focus on capturing short- to medium-term price movements, holding positions for several days to weeks. This differs from day trading, which involves opening and closing positions within a single day to capitalize on intraday price fluctuations.
What Makes a Good Swing Trading Strategy?
A good swing trading strategy uses technical indicators like the RSI (Relative Strength Index) to identify key entry and exit points. It combines market analysis with risk management to maximize potential gains while minimizing risks.
How Do Swing Traders Use Technical Indicators to Identify Opportunities?
Swing traders use technical indicators such as moving averages, RSI, and volume to identify potential swing trading opportunities. These indicators help traders determine the best times to enter and exit trades based on market trends and momentum.
What Role Does RSI Play in a Swing Trading Strategy?
RSI is a popular indicator used by swing traders to identify overbought or oversold market conditions. It helps traders spot potential entry and exit points by signaling when a market may be due for a reversal.
How Can Breakout Trading Be Integrated Into a Swing Trading Strategy?
Breakout trading involves identifying key levels where the price is likely to move significantly. Swing traders use breakout swing trading strategies to enter positions when the price breaks through resistance or support levels, aiming to capture the momentum of the breakout.
What Are the Key Indicators for Identifying Swing Trading Opportunities?
Key indicators for identifying swing trading opportunities include moving averages, RSI, MACD, and Bollinger Bands. These tools help traders analyze market trends, identify reversals, and determine optimal entry and exit points.
How Do Swing Traders Identify Key Entry and Exit Points in the Market?
Swing traders use a combination of technical analysis and indicators to identify key entry and exit points. They look for patterns such as breakouts, trend reversals, and support and resistance levels to make informed trading decisions.
What Is the Difference Between Breakout Swing Trading and Traditional Swing Trading?
Breakout swing trading focuses on capturing gains from price movements following a breakout above resistance or below support. Traditional swing trading may involve a broader range of strategies, including trend following and reversal patterns, to capitalize on various market conditions.
Join the CScalp Trading Community
Join our official trader's chat. Here you can communicate with other scalpers, find trading soulmates and discuss the market. We also have an exclusive chat for crypto traders!
Don't forget to subscribe to our official CScalp news channel, use trading signals and get to know our bot.
If you have any questions, just contact our platform's support via Telegram at @CScalp_support_bot. We will respond in a matter of seconds.
You can also visit our Discord channel and subscribe to the CScalp TV YouTube channel.
JOIN OUR CHAT
