Intraday Trading: A Comprehensive Day Trading Guide
Intraday trading, also known as day trading, involves the buying and selling of assets within a single trading day. This strategy aims to capitalize on small price fluctuations during normal trading hours. CScalp prepared a comprehensive guide on intraday trading, a strategy where every market movement could lead to a potential profit.
Attention! This article is for informational purposes only and does not contain recommendations or calls to action.
The review has been prepared by the CScalp terminal team. You can get CScalp by leaving your e-mail in the form below.
What Is Intraday Trading?
Intraday trading is a strategy that revolves around the buying and selling of assets within the span of a single day. Day traders seek to capitalize on the price fluctuations that happen during regular trading hours.
The term “intraday trading” originated in the stock market, where trading only occurs during specific hours on weekdays. Historically, day traders are market “employees” for the full day. In this style of trading, all positions are closed before the end of the “workday.”
In cryptocurrencies, the terms “day” and “night” are conditional. Trading can be done during the day or night – it all depends on the trader’s preferences. However, global markets correlate with each other, and the best trading opportunities open up during sessions in the American, European, and Asian markets.
Intraday Trading Strategy Overview
Once intraday traders’ working day commences, they identify assets they believe are currently undervalued but hold the potential for an upswing, as well as overvalued assets that could experience a decrease in their prices. Then they find entry and exit points and open a position using a professional trading terminal like CScalp.
The crux of intraday trading lies in closely monitoring how the price of the chosen cryptocurrency evolves throughout the day. When the asset’s price reaches a predetermined target for that day or approaches what the trader perceives as its intraday high or low, they close their position by selling the crypto. If the selling price exceeds the initial purchase price (inclusive of transaction fees), the trader secures a profit for the day.
CScalp intraday trading terminal
Intraday Trading and Market Volatility
Day traders need volatility. That means that the market has to move significantly in terms of percentage up and down during the day. Some markets (like cryptocurrencies and futures) are always volatile. Other instruments – most stocks, indices, and bonds – have low volatility and become volatile under certain conditions. Day traders also require liquidity, i.e., active trading at every given moment.
These are the time intervals during which global markets are most liquid and volatile:
- 1:00 – 7:00 UTC: opening and closing of the Asian trading session
- 9:00 – 12:00 UTC: premarket of the American session and the active phase of the European trading session
- 13:30 – 21:00 UTC: American session
- 23:30 – 00:30 UTC: closing of daily candles, a time with many market participants and potentially big trading volumes
- Typically, in the “evening” hours of the trading session, volumes and volatility are higher, as traders close their positions. Friday is an especially volatile day in the stock market: many traders close deals in anticipation of the weekend. This is partly to avoid encountering a gap. In general, the beginning and closing of the trading session are suitable for experienced traders (due to volatility). For beginners, engaging with the market in the middle of the trading day is more suitable.
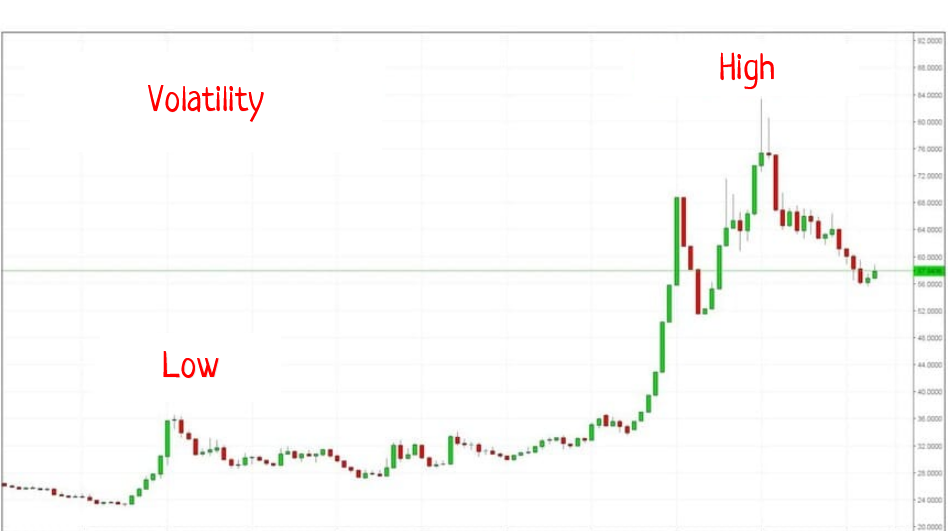
High and low volatility is shown on a cryptocurrency chart

Intraday Trading Challenges and Risks
Intraday trading is not a simple strategy. The high-speed nature of day trading demands meticulous attention to real-time charts, with short-term traders scrutinizing price movements down to the minute. The chosen intraday trading strategy, whether it be scalping or another approach, dictates the level of vigilance required.
Intraday traders must equally understand both fundamental analysis and technical analysis. Emphasis is placed on technical aspects. In search of trades, day traders are aided by chart patterns and candlestick patterns, price action analysis, order books, trading volumes, and technical indicators.
A day trader lives with the market. It is essential for a day trader to understand the market from the inside, knowing not only technical aspects but also fundamental driving forces. It’s crucial to comprehend macroeconomics, the media environment surrounding the market, and individual assets. Day traders need to constantly stay informed about news, and be able to react to them.
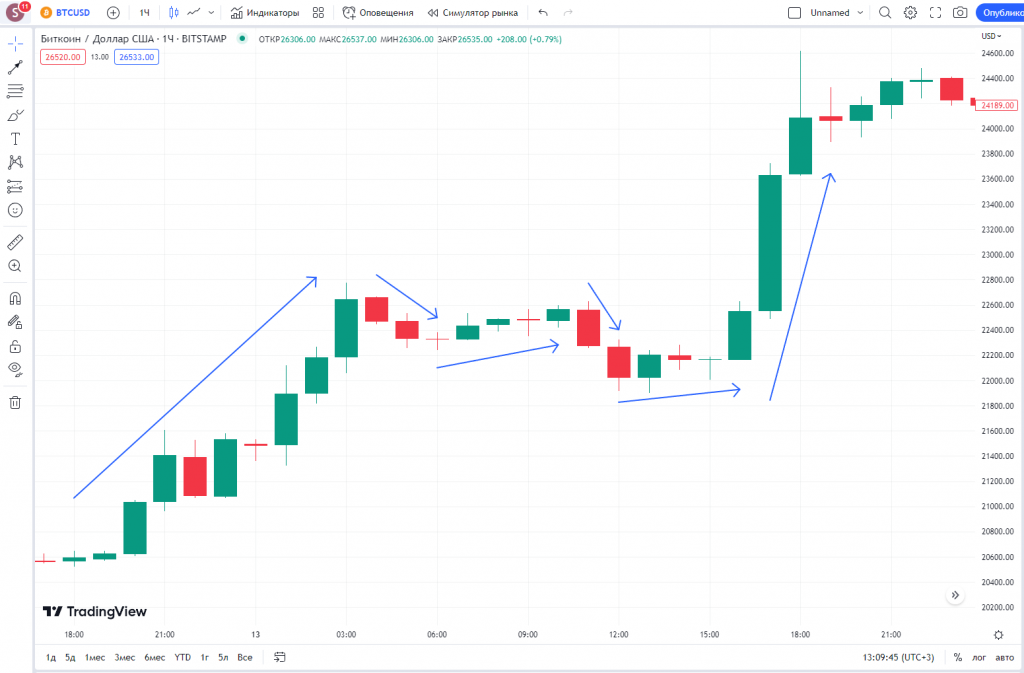
BTC/USDT Key price movements over a 24-hour period
Navigating the Intraday Terrain: Tools and Analysis
Intraday trading is not just about buying and selling within the confines of a single trading day; it’s a strategy that relies on a plethora of tools and analytical insights. At the core of an intraday trader’s arsenal are real-time charts, news reports, and an understanding of support and resistance levels.
Real-Time Charts: Decoding Market Dynamics
Example: Imagine you’re an intraday trader eyeing a particular asset. Real-time charts provide a visual representation of the asset’s price movements throughout the day, breaking down the data into intervals as short as one minute. These charts become the canvas on which traders paint their strategies, identifying trends, patterns, and potential entry or exit points.
News Reports: The Pulse of Market Volatility
Example: Let’s say breaking news about a major economic development hits the wires. Intraday traders keenly analyze these reports as they can significantly impact market sentiment. Positive news may trigger a surge in asset prices, while negative news could lead to a downturn. Being abreast of such developments allows intraday traders to align their positions with the prevailing market sentiment.
Support and Resistance Levels: Strategic Guideposts
Example: Picture a scenario where an asset has consistently bounced back from a certain price level (support) or struggled to surpass a specific value (resistance). Intraday traders use these historical patterns to make informed decisions. For instance, if an asset approaches a known resistance level, a trader might consider selling, anticipating a potential price drop.
Trading Signals: Exchange Information with Traders
In day trading, it is common to exchange ideas about where and when to open a trade. This is known as trading signals. Most signals (especially paid ones) directly tell you where to sell and where to buy, promising a “97% win rate.” We do not consider this approach sound. A signal is a hypothesis about where to find a trade. A signal should specify the basis for entry and the forecast of the target movement. The rest is up to the trader.
Find free day trading signals and scalping signals on CScalp’s Discord server. Signals are created by experienced traders and undergo our team’s moderation. Signals are open for comments, allowing you to read other traders’ opinions about them and leave your own. Remember that a signal is the subjective opinion of another trader. Signals should not be regarded as a directive for action, and trades should not be opened “blindly.” A signal is used as a source of ideas, to confirm or refute one’s analysis. Any signal may fail to perform as expected.
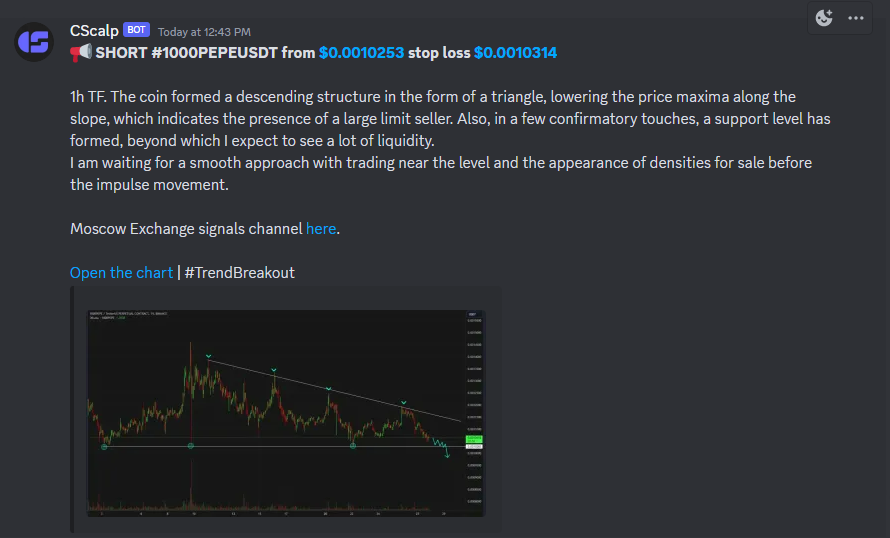
A free intraday trading signal PEPE/USDT on CScalp’s Discord server
Intraday Trading Strategies: Tailoring Approach to Goals
The landscape of intraday trading is vast, and traders must select a strategy that aligns with their goals, risk tolerance, and lifestyle.
Scalping: Swift and Precise Movements
Scalping is akin to a financial sprint, involving the execution of numerous small trades throughout the day to exploit minimal price differentials. This strategy thrives on the immediacy of short-term market movements, requiring traders to act swiftly and with precision.
Example: Imagine an asset whose price experiences micro-fluctuations within minutes. A scalper might seize the opportunity to buy low and sell high, capturing small profits in rapid succession. The goal is not to ride long-term trends but to capitalize on the quick, often fractional, price shifts.
Range Trading: Riding Support and Resistance Waves
Range trading centers on identifying an asset’s support and resistance levels – price points where it historically tends to bounce back or stall. Traders then strategically buy at support and sell at resistance, profiting from predictable price movements within the established range.
Example: Consider an asset oscillating between $50 (support) and $55 (resistance). A range trader might initiate a buy order when the asset approaches $50, anticipating an upward rebound. Conversely, they could sell near $55, expecting the price to recede. Range trading is effective when an asset’s price adheres to well-defined boundaries.
News-Based Trading: Capitalizing on Market Dynamics
News-based trading involves closely monitoring significant events that impact financial markets. Traders aim to capitalize on resulting price changes triggered by breaking news, economic reports, or geopolitical developments.
Stock Market Example: Suppose a pharmaceutical company announces a breakthrough in drug development. News-based traders might swiftly respond by buying shares in anticipation of an asset price surge. Conversely, negative news, such as a regulatory setback, could prompt selling to avoid potential losses. This strategy requires rapid decision-making based on the unfolding news landscape.
High-Frequency Trading: Algorithms in Action
High-frequency trading (HFT) employs algorithms and advanced technology to execute numerous orders at exceptionally high speeds. HFT seeks to profit from short-term market inefficiencies or anomalies, relying on algorithmic precision.
Example: Picture a scenario where an asset’s price momentarily diverges. HFT algorithms swiftly detect this discrepancy and execute trades to exploit the price difference, often within fractions of a second. While individual gains per trade may be minimal, the cumulative effect of numerous rapid trades can be substantial.
Intraday trading strategies offer diverse approaches to navigating the financial markets. Traders select the strategy aligning with their risk tolerance, market insights, and preferred trading style, recognizing that each strategy has its unique set of challenges and rewards
Unveiling Intraday Trading Strategies: A Comprehensive Exploration
In the intricate world of intraday trading, various strategies exist, each tailored to different market conditions and trader preferences. Learn more about this on our blog “Scalping vs. Intraday Trading: Which Approach Suits You Best?”.
Intraday vs. Interday Trading: What Are the Differences?
Intraday Trading
Intraday trading is a tactical approach centered on navigating price fluctuations within the confines of a single trading day. Traders engaged in intraday activities aim to open and close positions capitalizing on short-term market movements. This strategy demands keen attention to real-time data and the ability to make rapid decisions in a dynamic trading environment.
Example: An intraday trader monitoring an asset observes a sudden surge in market demand after a positive report about a cryptocurrency. Recognizing the potential for a short-term price increase, the trader executes a buy order and closes the position before the market closes to secure a same-day profit.
Interday Trading
Interday trading extends the time horizon beyond a single day, encompassing trades that span multiple days or even weeks. Interday traders consider longer-term trends, allowing for a more patient and strategic approach to decision-making.
Example: An interday trader assessing a crypto company’s growth prospects decides to hold a position for several days. This approach allows the trader to capitalize on sustained upward momentum as the company announces successive positive developments, optimizing gains over a more extended period.
In the dichotomy of intraday and interday trading, traders must weigh the benefits of rapid, short-term gains against the potential for more extended, trend-driven profitability. The choice between these approaches hinges on individual risk tolerance, market outlook, and the time commitment a trader is willing to dedicate to their craft.
Intraday Trading Formula
In the realm of intraday trading, the Pivot Point Theory stands out as a robust formula guiding traders through the dance of asset movements within a trading day.
Pivot Point Theory in Intraday Trading
This mathematical approach harnesses key metrics, including the intraday high, intraday low, and closing price, to unveil potential trajectories in the market.
The Mechanics of Pivot Point Theory
At its core, the Pivot Point Theory employs a straightforward formula:
Intraday High (H) + Intraday Low (L) + Closing Price (C) = X
Intraday High (H)+Intraday Low (L)+Closing Price (C)=X
Once this value, X, is obtained, it is divided by 3 to calculate the pivot point (P). Finally, the pivot point is multiplied by 2.
Making Sense of the Formula
- Intraday High (H): The highest price an asset reaches during a trading day.
- Intraday Low (L): The lowest price an asset dips to within the same trading day.
- Closing Price (C): The final traded price of the asset as the market closes.
Example Application
Consider a scenario where an asset has an intraday high of $60, a low of $40, and closes at $50. Applying the pivot point formula:
- P= (60+40+50)/3
- P= 150/3
- P=50
Finally, multiplying the pivot point by 2:
- Pivot Point×2=50×2=100
In this example, the calculated pivot point is $50, and the resulting value of $100 becomes a reference point for the trader.
Interpreting Pivot Points
Above Pivot (P): If an asset is trading above its pivot point, the theory suggests an inclination towards an upward trajectory until it encounters resistance.
Below Pivot (P): Conversely, if an asset is below the pivot point, the theory posits a potential downward movement until it reaches support levels.
While the Pivot Point Theory doesn’t guarantee future price movements, it serves as a valuable tool for intraday traders to assess potential entry and exit points based on historical performance.
Rules for Intraday Trading: Regulation of Stock Brokers and Their Customers
Regulatory Framework
Adherence to regulatory guidelines is paramount in the intraday trading of stocks. The Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) takes center stage in shaping the landscape for traders. FINRA’s intraday trading rules, commonly known as the “Pattern Day Trader” (PDT) rules, apply to all U.S. stockbroker-dealers and their customers.
Minimum Equity Requirements
FINRA defines and imposes specific rules on a subset of intraday traders known as pattern day traders. To fall into this category, a person must execute four or more day trades within a five-business-day rolling period. Furthermore, these day trades must represent over 6% of the person’s total margin account trades during that period.
For pattern day traders, maintaining a minimum equity requirement becomes obligatory. This stipulates that the trader must have at least $25,000 in their account before engaging in any day trades. This minimum amount must be preserved at all times. Should the account fall below this threshold, the trader loses the privilege to engage in day trading
.
Day Trading Buying Power Restrictions
Pattern day traders are subject to restrictions on their day trading buying power. They are allowed to trade up to four times the value of their maintenance margin excess at the closing bell of the previous day. Should a trader breach this rule, their broker-dealer is obligated to issue a day trading margin call.
Margin Risk
Margin accounts are a common tool for intraday traders, providing them with the leverage to amplify their trading potential. However, this approach introduces a notable risk factor known as margin risk.
The Margin Call Conundrum
Intraday traders utilizing margin accounts must be wary of margin calls. A margin call occurs when a trader borrows more money than is available in their brokerage account. In such a scenario, the broker demands the repayment of the borrowed amount.
Meeting Margin Calls
Under FINRA rules, traders have a five-business-day window to meet their margin call. During this period, they are restricted to trading up to two times their maintenance margin excess. For instance, if a margin call is issued with a maintenance excess of $30,000, the trader can continue trading for five days, but their trades are capped at $60,000.
Extended Restrictions for Non-Compliance
Failure to meet a margin call within the specified period results in extended restrictions. The trading account is limited to transactions on a cash-available basis only for 90 days or until the margin call is satisfied. This implies that the trader can only execute trades using the cash available in their account and is prohibited from borrowing funds.
Is Intraday Trading a Good Idea?
Understanding the nuances of this trading strategy is essential, and to do so, we’ll first dissect the inherent advantages and disadvantages that shape the landscape of intraday trading. Join us as we unravel the complexities, weigh the considerations, and delve into the heart of the intraday trading experience.
Intraday Trading Pros and Cons
Intraday Trading Advantages
- Avoiding Overnight News Impact: One of the distinct advantages of intraday trading is the ability to sidestep the impact of overnight news. By closing positions before the market closes, intraday traders shield themselves from potential market shocks that often occur overnight. This agility allows for a more controlled and measured approach to trading.
- Potential for Big Rewards: Intraday trading has the potential for substantial rewards. Leveraging margin accounts provides traders with increased buying power, allowing them to capitalize on even minor price fluctuations. The ability to generate quick profits in a single day can be enticing for those seeking an active and potentially lucrative trading experience.
Intraday Trading Disadvantages
- Higher Commission Costs: Intraday trading comes with higher commission costs. The frequency of opening and closing positions, coupled with the need for swift execution, can lead to increased transaction fees. Traders must factor these costs into their overall strategy, potentially impacting overall profitability.
- Market Uncertainties: The fast-paced nature of intraday trading exposes traders to market uncertainties. Sudden price movements, unexpected news, or changes in market sentiment can lead to unpredictable outcomes. Novice traders may find it challenging to navigate these uncertainties effectively.
Considerations Before Starting Your Intraday Trading Journey
- Download and Install Free Professional Trading Platform: Before embarking on your intraday trading journey, it’s essential to equip yourself with the right tools, and one such crucial tool is a professional trading platform. CScalp is a notable example of a free, professional trading platform specifically tailored for day traders.
- Access to a Margin Account: Access to a margin account provides traders with the ability to amplify their trading potential. However, it introduces margin risk, including the possibility of margin calls. Traders must carefully assess their risk tolerance and ability to manage margins responsibly before engaging in intraday trading.
- Market Knowledge: Intraday trading demands a solid understanding of market dynamics, technical analysis, and trading strategies. Traders relying on short-term price fluctuations must be adept at interpreting real-time charts, news reports, and support/resistance levels. Continuous learning and staying informed about market trends are integral to success.
- Time Commitment: Effective intraday trading requires a significant time commitment. Traders must dedicate their attention to real-time market movements, news updates, and chart analysis throughout the trading day. This level of commitment is often challenging for those with other professional or personal obligations.
Navigating the Intraday Trading Realm: A Strategic Conclusion
Intraday trading unveils a world of opportunities and challenges. In this landscape, success hinges on more than just market acumen – it demands careful consideration and astute risk management.
Success in the fast-paced realm of intraday trading requires not only a keen understanding of market dynamics but also a commitment to diligent risk management. The potential for rewards is enticing, but it is the thoughtful and calculated approach that truly sets the stage for triumph. Happy trading!
Join the CScalp Trading Community
Join our official trader's chat. Here you can communicate with other scalpers, find trading soulmates and discuss the market. We also have an exclusive chat for crypto traders!
Don't forget to subscribe to our official CScalp news channel, use trading signals and get to know our bot.
If you have any questions, just contact our platform's support via Telegram at @CScalp_support_bot. We will respond in a matter of seconds.
You can also visit our Discord channel and subscribe to the CScalp TV YouTube channel.
JOIN OUR CHAT
