Smart Money Concepts in Trading: Strategy, Market Structure, and Definition
Smart money concepts refer to strategies and techniques used by experienced and institutionally informed investors or traders, often referred to as “smart money,” to make investment decisions. These participants are considered to have a better understanding of the market, access to comprehensive information, and the ability to influence market movements. CScalp explores the Smart Money strategy, breaks down its key concepts, and examines the market patterns.
Attention! This article is for informational purposes only and does not contain recommendations or calls to action.
The review has been prepared by the CScalp terminal team. You can get CScalp by leaving your e-mail in the form below.
What Is Smart Money in Trading?
The Smart Money strategy serves as an analytical tool to interpret the actions of major market players. It’s relevant across diverse markets, such as stocks and cryptocurrencies, highlighting entities with significant capital – like banks and hedge funds, often referred to as “whales.” These players, with their profound capital resources and market knowledge, have a deeper insight into market dynamics compared to the average market participant. Their substantial capital and expertise not only allow them to understand market nuances better, but also give them the power to influence market directions to their advantage.
While there are numerous interpretations of Smart Money concepts, differing across various sources. Various discussions exist regarding which practices can be classified under Smart Money strategies and which cannot. We aim to illuminate the most universally recognized elements of this strategy, offering insights into how influential market players operate, and give a comprehensive description of the Smart money tools.
Smart Money Concept
The essence of the Smart Money approach is grounded in the theory that in the market, there are “smart players” and the “crowd.” The “smart players” influence the market to their advantage. The “crowd” is reactive and follows the “smart players,” usually unconsciously. The goal is to decipher the truth behind the strategies of these big players and align their trades with them, aiming to capitalize on the consequential market movements.
Unlike large players, the crowd can trade quickly. There is always enough volume (liquidity) in the market to execute retail orders. The average trader can place an order in a liquid market without worrying about its execution.
The circumstances for “smart players” differ significantly. A large player cannot quickly execute an order because of its volume. Significant liquidity is needed for their order to be filled. This liquidity is provided by the orders of the “crowd” – large players “accumulate” it. Consequently, “smart players” engineer scenarios that compel the “crowd” to respond by buying or selling, influencing supply and demand dynamics.
Large participants work gradually: they cannot “unload” the entire order at once, so they “unload” it in small parts. Usually, this is a lengthy process that can take days or even weeks.
To take full advantage of smart money concepts, try the professional trading platform CScalp by leaving your email in the form above. With the free terminal, you will be able to connect to an exchange and place orders with one click, automatically set Stop-Loss and Take-Profit targets, as well as manage your risks.
Smart Money Market Structure Patterns
Let’s conduct a detailed analysis of the main patterns, formations, and phenomena that are crucial to the Smart Money strategy, providing a deep understanding of the mechanisms governing the market.
Market structure
Structure in Smart Money usually refers to an upward movement, a downward movement, or a sideways (flat) movement of the market, each indicating distinct phases of market sentiment and participant behavior.
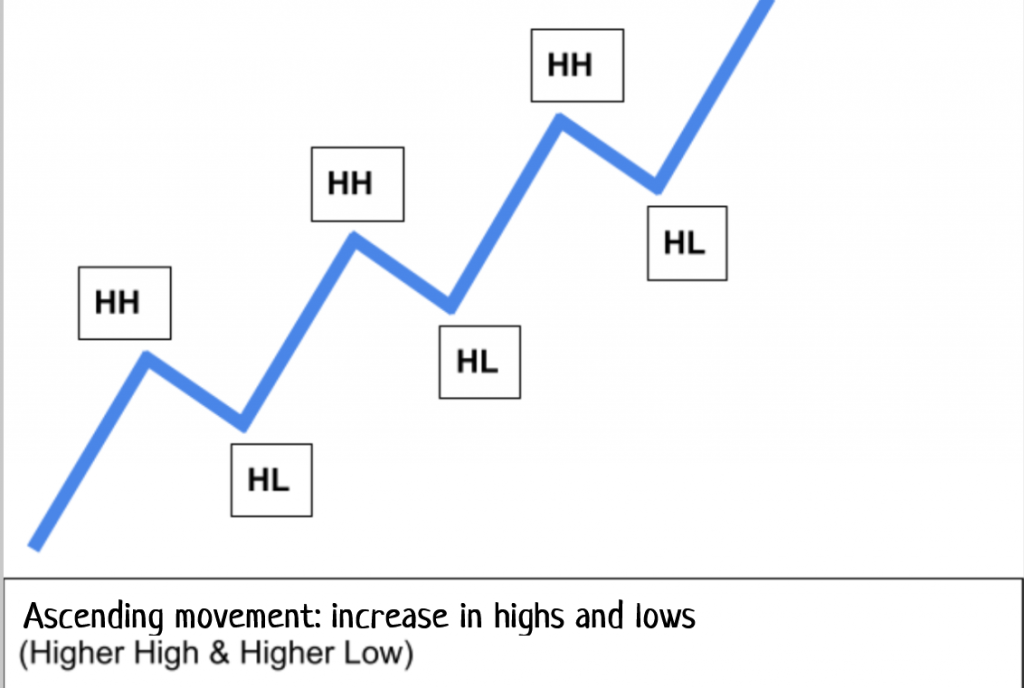
In an uptrend, lows and highs increase. /CScalp
An upward movement is characterized by increasing local lows and highs.
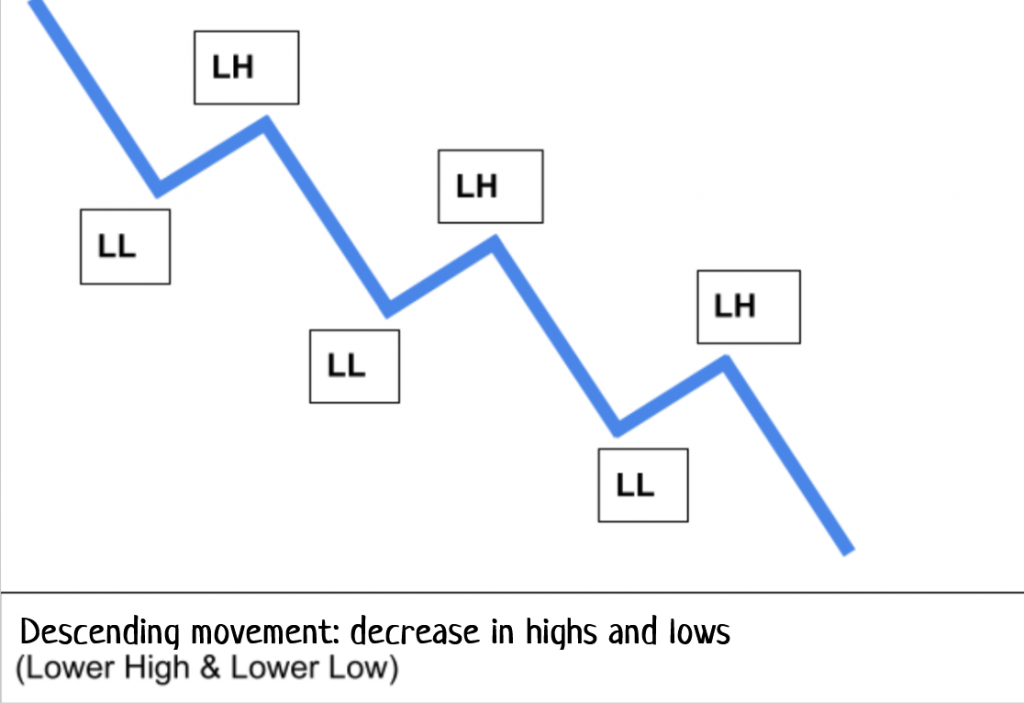
In a downtrend, lows and highs decrease. /CScalp
A downward movement is characterized by decreasing local lows and highs.

In a sideways movement, lows and highs do not change. /CScalp
A sideways movement is defined by its absence of a definitive trend, fluctuating within a confined range.
Structures can be divided into primary and secondary.
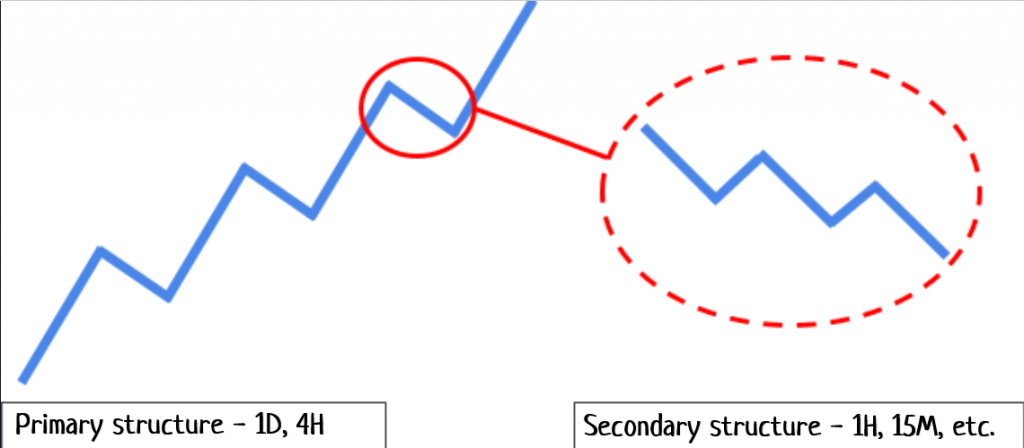
Primary structures include shorter-term secondary ones/ CScalp
Primary structures represent global trends that can be observed on 1-day and 4-hour timeframes (TF). Secondary structures are smaller-scale movements occurring within primary structures. They are identifiable on lower TFs – 1h, 15m, etc. The market is fractal: within a primary upward structure, secondary downward ones occur, and vice versa.
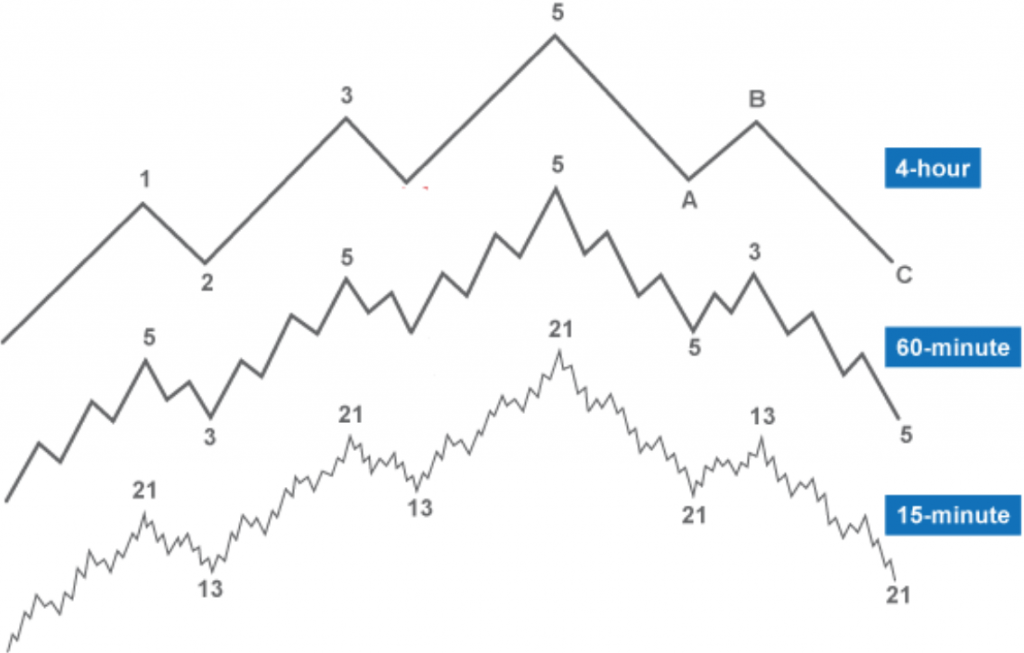
In an uptrend, downward “secondary” movements occur, and vice versa/ CScalp
Break of Structure refers to an instance where the subsequent high (H) or low (L) contradicts the prevailing market structure.
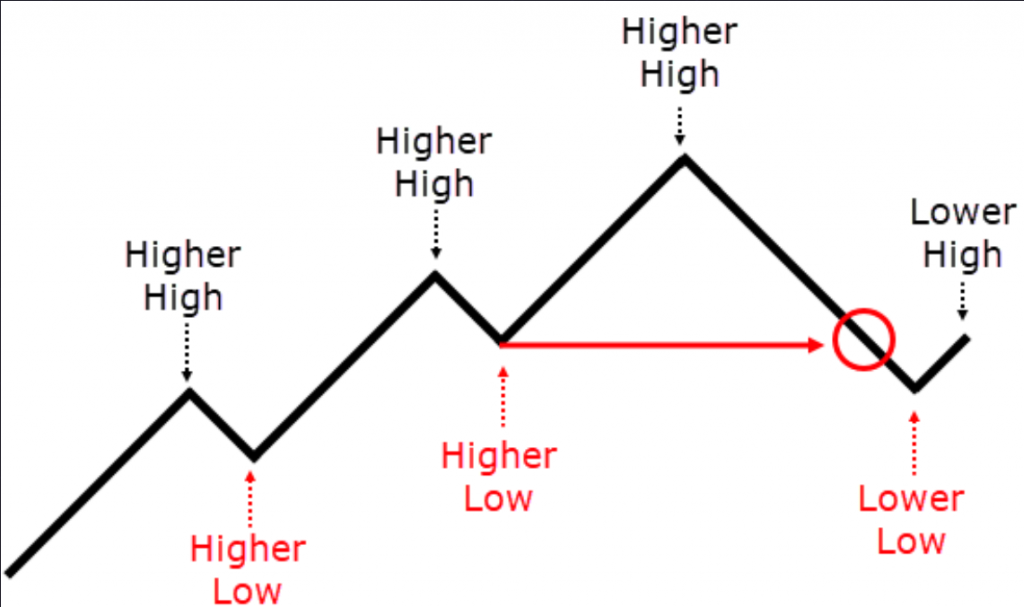
Break of structure: the departure of the next High or Low against the current structure. In the example – a break in an uptrend./ CScalp
For instance, within an upward structure, a break occurs when the forthcoming minimum decreases, contrary to the expected increase. This is only considered a break if the preceding maximum is greater than its predecessor. Without this condition, it’s not recognized as a break.
Conversely, in a downward structure, a break is identified by an increase in the upcoming maximum, which deviates from the anticipated decrease. This is valid only if the preceding minimum is less than the one before it; otherwise, it’s not acknowledged as a break.
Within the Smart Money strategy, trading positions are initiated following the direction of the primary structure, and it’s generally inadvisable to place trades that go against this prevailing trend.

Liquidity
One of the Smart Money concepts, liquidity refers to the orders of the “crowd” needed to “absorb” the orders of large players. The most significant source of liquidity is the Stop-Loss orders of small participants. The “crowd” bases its trading decisions on technical analysis, utilizing methods like identifying trends and recognizing support and resistance levels, among other strategies.

Liquidity, needed by large players, is located beyond levels and trend lines./ CScalp
Since retail traders typically set their Stop-Loss orders near crucial levels, either just above or below trend lines or within the bounds of sideways channels, large market participants often aim to activate these stops. When these Stop-Loss orders are triggered, they help to accommodate the volume handled by the “smart players.”
In Smart Money terminology, “liquidity pools” refer to areas dense with liquidity originating from smaller market participants. These pools often consist of aggregated Stop-Loss orders situated beyond the confines of channel limits and trend lines.

Liquidity capture, false breakouts./ CScalp
Large market players strategically maneuver the price towards a “pool” to accumulate liquidity from the crowd, a tactic known as “liquidity capture” or “liquidity grab.” This maneuver is depicted on charts as a ‘spike’ or false breakout, where the price momentarily surpasses a defined level, only to retreat to its prior range, and frequently, it moves even further. By executing this strategy, large players harness the liquidity accumulated through the crowd’s Stop-Loss orders. If the liquidity is sourced from below the current price level, they initiate long positions; if it’s from above, they opt for short positions, thus capitalizing on the gathered liquidity to drive their market strategies.
Imbalance
Imbalance in trading is identified by a specific formation of three candles on a chart: a long impulse candle, which doesn’t prompt an immediate market reaction, is flanked by two shorter candles, one on each side. This setup suggests a significant move in the market, with the longer candle indicating a strong buying or selling pressure that was not counteracted, while the shorter candles imply lesser market activity before and after the impulse.
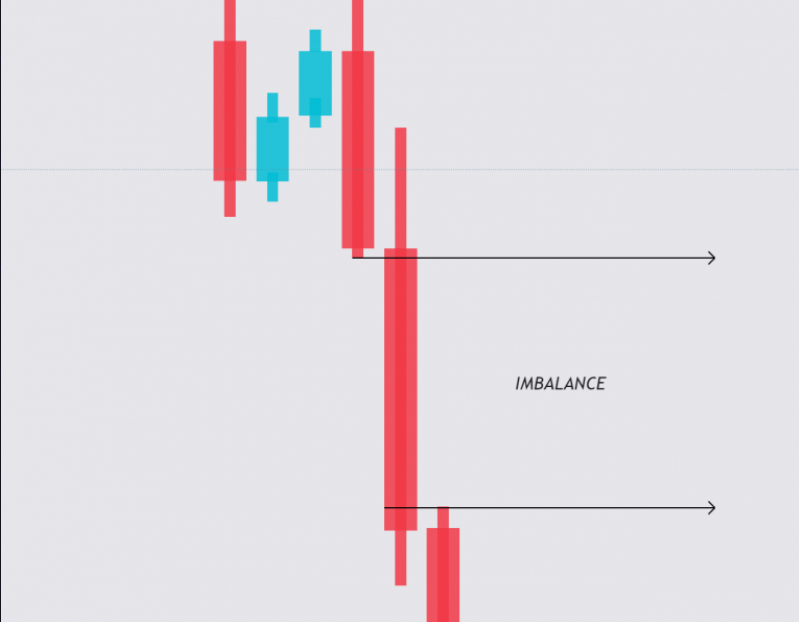
Imbalance – a long candle, “breaking” two adjacent ones./ CScalp
In an imbalance formation, the key feature is the long candle at the center, encircled by two shorter candles. The essential condition for recognizing an imbalance is the distinct separation between the wicks of the side candles and the body of the central candle. This separation indicates that the market momentum represented by the long candle was not matched by subsequent trading periods. If the wicks of the side candles overlap with the body of the central candle, then the setup does not meet the criteria for an imbalance, as this overlap suggests a continuity of market sentiment rather than a distinct shift.
Imbalances are widespread on the market. On the chart – a partially covered imbalance. /CScalp
Imbalances in the market can exhibit varying degrees of coverage: fully covered, partially covered (often halfway), or not covered at all. When we talk about an imbalance being “covered,” it implies that subsequent trading activity has occurred within the price range defined by the body of the long candle of the imbalance formation. This trading activity effectively fills in the price gap that was created, bringing the price back to the starting point of the imbalance. The concept of coverage is crucial in determining the potential future behavior of the market concerning these imbalances.
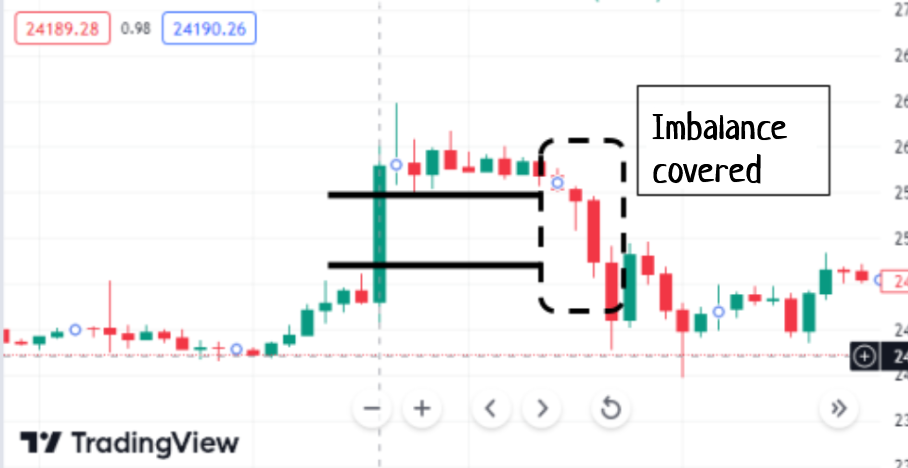
The coverage of an imbalance is trading within the range created by the imbalance candlestick. /CScalp
An impulse candle is indicative of a significant volume trade executed by a large market player, reflecting a strong movement in price. Following this, to realign the market balance and potentially close out positions, the large player may instigate market movements aimed at “covering” the imbalance zone.
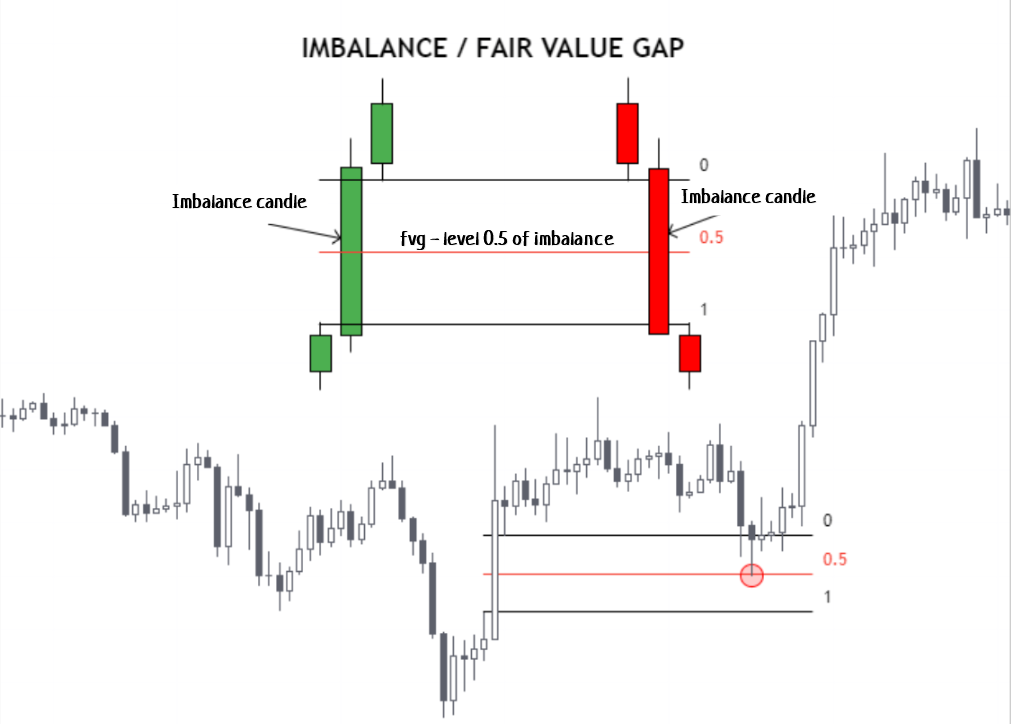
Imbalances serve as attractors, “magnets” for price rather than direct entry points. They can be strategically evaluated alongside Order Blocks and the prevailing market structure to pinpoint potential entry opportunities. The area of imbalance is frequently assessed using the 0.5 Fibonacci retracement level to gauge market reactions.
Since market prices often move to fill or “cover” the imbalance, this area can be strategically used as a take-profit zone. Particularly on shorter timeframes, initiating a trade at the midpoint of the imbalance’s coverage is a tactic considered by traders. In Smart Money trading methodologies, it’s common to enter trades based on the expectation that the price will move to cover the imbalance, thereby capitalizing on this predictive movement.
It’s important to note that within the Smart Money framework, the term “imbalance” is interchangeably referred to as “disbalance,” FVG (Fair Value Gap), Void, or Liquidity Gap. However, this concept should not be conflated with a “market gap,” which is a different phenomenon characterized by a break between trading sessions, visible as a space between candlesticks on a chart.
Order Block
An order block refers to the final bullish candle observed before a substantial market decline or the last bearish candle that appears before a significant upward movement. This concept is key in identifying potential reversal points and understanding the sentiment shifts within the market, as these candles often indicate the accumulation of orders from large players before a major price direction change.
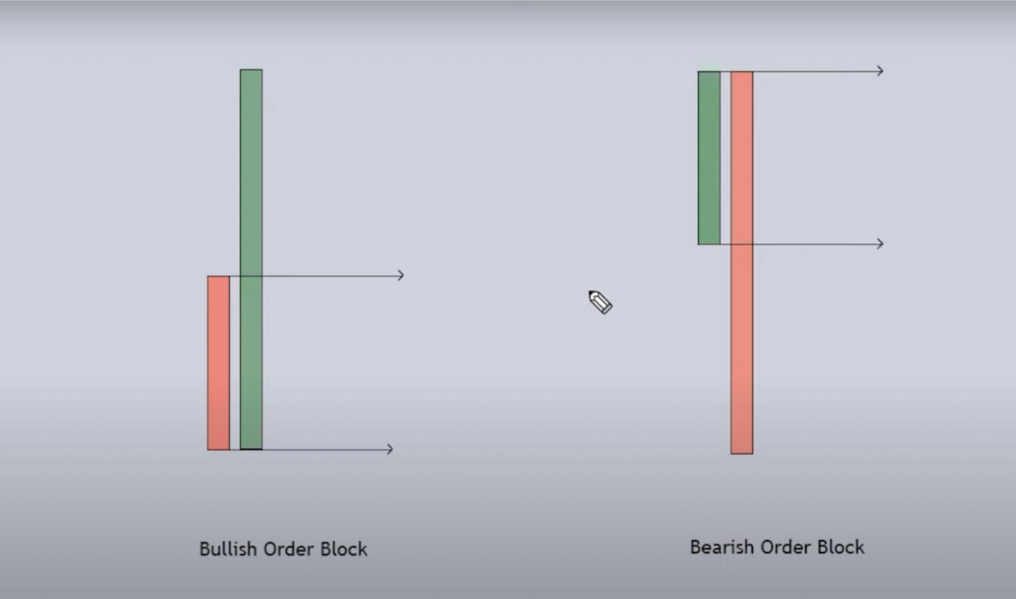
A schematic view of an order block. /CScalp
On occasions, candles that share the same color as the ensuing market movement may also be identified as order blocks. For an order block to be deemed valid, it ideally should be situated at or close to support or resistance levels. This positioning underscores the significance of the order block, as it aligns with crucial market thresholds where significant buying or selling interest is anticipated, thereby offering strategic insights for traders.
Price moves away from the order block but eventually returns to its zone. /CScalp
The area formed by the order block functions similarly to the Point of Control (Point of Control) in the “Market Profile” indicator. The PoC is recognized as a key focal point for substantial market players because it represents the price level with the most trading activity over a given time. Similar to the PoC, an order block acts as a gravitational point for the price, drawing it back after a significant movement.
To illustrate the dynamics of an order block, consider a scenario involving a downward market movement. In this case, “smart money” entities place large sell orders, which are initially bought up by the “crowd,” causing a temporary rise in the asset’s price. Retail traders, interpreting this rise as a sign of continued upward momentum, may enter long positions. Subsequently, when “smart money” players execute another large sell order, the market shifts downward, aligning with their strategic positioning. Upon the market reaching the end of this downward trajectory, “smart money” realizes profits from their short positions. Meanwhile, the “crowd,” now at a higher entry point, tries to offset losses by driving the price up, which inadvertently aligns with “smart money” interests, pulling the price back toward the order block.
In this context, order blocks should not be used as standalone entry points. They are most effective when aligned with the primary market structure. An order block suggesting a bullish move in a predominantly bearish market should be approached with caution. Furthermore, placing stop losses just outside the order block zone – above for short positions and below for long positions – can offer a strategic safeguard against adverse market movements.
To learn more about this topic, check out this article in our blog: “What Is an Order Block: Trading Strategies and Definition.”
More About Smart Money Analysis
One of the critical aspects of leveraging Smart Money strategies is the ability to identify and follow the “footprints” left by major players. This involves analyzing market patterns, volume, price action, and other indicators. By understanding where Smart Money is moving, traders can align their strategies to capitalize on the momentum generated by these entities. Important things to consider:
- Volume and Price Action: Smart Money often operates in volumes significant enough to shift market trends. Observing volume spikes alongside price movements can provide clues to Smart Money’s presence. A sudden increase in volume, coupled with a notable price change, can often signify Smart Money entering or exiting a position.
- Market Manipulation Awareness: While “manipulation” may carry a negative connotation, it’s a prevalent aspect of how Smart Money operates. These players have the capital to influence market directions in their favor, temporarily creating deceptive signals that can trap unsuspecting traders. Understanding these tactics can help traders avoid common pitfalls and align their trades with the actual market direction intended by Smart Money.
- Patience and Discipline: Emulating Smart Money means adopting a patient and disciplined approach to trading. Smart Money doesn’t chase the market; it sets positions where players anticipate the market will move. Traders should cultivate the ability to wait for the right conditions that signal a Smart Money move, rather than making impulsive decisions based on fleeting market trends.
- Technological Tools: Utilizing trading tools and platforms can enhance a trader’s ability to find all needed data and follow Smart Money movements. Software that analyzes market trends, highlights volume anomalies and offers real-time charting can provide valuable insights that inform smarter trading decisions.
- Risk Management: Like any trading strategy, following Smart Money isn’t foolproof and needs to be supported by fundamental analysis. It’s imperative to employ stringent risk management tactics, ensuring that even if a trade doesn’t align with Smart Money’s anticipated move, the loss is contained and manageable. Utilize Stop-Losses to define your risk threshold on each trade and stick to them rigorously. A common approach is the 2% rule, which suggests not to risk more than 2% of your capital on a single trade. Remember that CScalp has implemented an automatic Stop-Loss feature that you can use to protect your assets.
To learn more about Smart Money trading strategy secrets, check out the following video from our YouTube channel, CScalp TV:
Gain More Knowledge on Smart Money Trading Strategy
The market is a dynamic entity, continuously evolving with each trading session. Keeping abreast of financial news, market analysis, and the broader economic environment can provide a deeper context for Smart Money’s actions and help traders adapt their strategies to shifting market conditions.
- Explore a free crypto scalping course from the CScalp team. The CScalp team knows that newcomers are going through many obstacles and provides some of the best education in this field. The Internet has a huge amount of information, but there is a high probability that you won’t find anything useful there. The course is designed to help novice traders with a clear algorithm of actions.
- Explore the educational content provided by experts on social media, for example, the CScalp TV YouTube channel. In the videos, they delve into typical market scenarios orchestrated by large players, offering retail traders insights into the strategies and maneuvers employed by these influential market participants.
- CScalp has created a free online Trading Diary which will help you keep track of your cryptocurrency trading results. This online tool allows you to review trade history and correct your trading strategy while learning from your mistakes, discovering new approaches to trading, and gaining experience.
Smart Money Concepts – Conclusion
The Smart Money concept, while relatively novel in the trading arena, is swiftly gaining traction among traders. It is often lauded for its robustness, offering valuable perspectives on common dilemmas faced by retail traders, like frequent stop-outs or price movements that defy entry expectations. This strategy advocates for aligning trades with the actions of significant market players, potentially enhancing trade execution efficiency.
However, it’s crucial to acknowledge that employing the Smart Money approach does not assure successful or profitable trading automatically. The effectiveness of this strategy significantly hinges on the trader’s skill level and psychological approach to the market.
Frequently Asked Questions: FAQs About Smart Money Concepts
What Are Smart Money Concepts in Cryptocurrency Trading Strategy?
Smart Money concepts involve analyzing and understanding the trading behaviors and strategies of experienced and well-capitalized market participants, like institutional investors, to inform one’s trading decisions in the cryptocurrency market.
How Can One Apply Smart Money Concepts to Identify Market Trends in Crypto?
One can apply Smart Money concepts by monitoring large transaction volumes, significant price changes, and accumulation patterns, which may indicate the presence and market direction of Smart Money players.
Do Smart Money Concepts Differ When Applied to Bitcoin Versus Altcoins?
The core concepts remain the same, but the impact and visibility of Smart Money might vary due to the different market capitalizations and liquidity profiles of Bitcoin compared to altcoins.
Why Is Liquidity an Important Smart Money Concept?
Liquidity is key because it ensures that Smart Money can execute large trades with minimal slippage, and their actions are more pronounced and identifiable in liquid markets, providing clearer signals for other traders.
How Can Traders Distinguish Between Smart Money Actions and Market Manipulation in Crypto?
By combining volume analysis with contextual market information, traders can discern whether a movement is a genuine Smart Money strategy or potentially manipulative, looking for consistent patterns over isolated incidents.
Can Understanding Smart Money Concepts Improve Risk Management in Crypto Trading?
Absolutely. By recognizing and aligning with Smart Money movements, traders can make more informed decisions, improving entry and exit points, which enhances risk management and potential profitability.
Are Certain Smart Money Patterns More Prominent in Crypto Trading Compared to Traditional Markets?
Yes, due to the nascent and highly volatile nature of the crypto market, certain Smart Money patterns, like rapid accumulation phases and strategic liquidity plays, can be more apparent compared to traditional markets. Additionally, these patterns are often analyzed using a forex trading platform, further aiding traders in their strategy development.
How Can Understanding Smart Money Concepts Contribute to Safe Financial Decisions in Cryptocurrency Trading?
Understanding smartmoney concepts allows traders to make safer financial decisions by aligning their strategies with those of well-informed, influential market players. By identifying and following the actions of these “smart financial players,” traders can adopt safe and more strategic approaches. This enables them to better anticipate market movements, manage risks more effectively, and make informed decisions that align with underlying market trends, reducing the likelihood of making uninformed or risky trades.
Join the CScalp Trading Community
Join our official trader's chat. Here you can communicate with other scalpers, find trading soulmates and discuss the market. We also have an exclusive chat for crypto traders!
Don't forget to subscribe to our official CScalp news channel, use trading signals and get to know our bot.
If you have any questions, just contact our platform's support via Telegram at @CScalp_support_bot. We will respond in a matter of seconds.
You can also visit our Discord channel and subscribe to the CScalp TV YouTube channel.
JOIN OUR CHAT
