What Is Bitcoin? Definition, Blockchain Technology, Cryptocurrency Landscape
Bitcoin is the first cryptocurrency in the world. It operates independently of traditional banking and governmental oversight. CScalp delves into the idea behind Bitcoin, how the blockchain network and BTC cryptocurrency work, as well as into the risks and disadvantages of the first cryptocurrency.
Attention! This article is for informational purposes only and does not contain recommendations or calls to action.
The review has been prepared by the CScalp terminal team. You can get CScalp by leaving your e-mail in the form below.
First-Ever Cryptocurrency: Bitcoin Definition and Ideology
Bitcoin is the first cryptocurrency that was designed to facilitate fast, free, and anonymous money exchanges, mirroring the Internet’s impact on information sharing.
The inception of Bitcoin can be traced back to an enigmatic figure (or possibly a group) known as Satoshi Nakamoto. In 2008, Nakamoto introduced the Bitcoin White Paper, a seminal document that delineated the core principles of the Bitcoin network and its cryptocurrency. This white paper galvanized a cohort of developers, fostering a collaborative environment that brought Bitcoin’s concepts to fruition.

Satoshi Nakamoto’s White Paper
On January 9, 2009, the Bitcoin network officially commenced operations. Following its launch, Nakamoto maintained communication with the burgeoning Bitcoin community but eventually vanished, leaving no trace of their identity.
Bitcoin.org has become the steward of the Bitcoin network, offering resources and guidance for users and developers. This decentralized nature of Bitcoin is a testament to its foundational philosophy: to create a financial system where transactions are not just transparent, but also equitable and liberated from centralized control.
The inception of Bitcoin marked a pivotal moment in financial history, proposing an alternative to the traditional monetary system. Its blockchain technology – a decentralized ledger recording all transactions – has inspired a multitude of other digital currencies (altcoins) and blockchain-based innovations. As Bitcoin continues to evolve, it challenges conventional notions of money, prompting a reevaluation of the mechanisms underpinning financial transactions and value exchange in the digital age.
To take full advantage of trading Bitcoin, try the professional trading platform CScalp by leaving your email in the form above. With the free terminal, you will be able to connect to your preferred exchange and place orders with one click, as well as automatically manage your risks.
Peer-To-Peer Framework and Blockchain Technology
At its core, Bitcoin thrives on a decentralized peer-to-peer framework, utilizing blockchain technology to create a transparent and secure financial ecosystem. Bitcoin combines its network cryptocurrency and blockchain to record transactions, essentially as a public ledger, ensuring that data is accessible in real time.
All transaction data is public and can be viewed by anyone using blockchain, yet it remains completely anonymous. The Bitcoin network does not collect its users’ data: it operates through a system of addresses generated by the system itself. An example of a Bitcoin wallet address is bc1qxy2kgdygjrsqtzq2n0yrf2493p83kkfjhx0wlh.
Each Bitcoin wallet has a unique address, known as the “Public key,” coupled with a “Private key,” akin to a username and password in digital banking. These are cryptographic keys that act like a login and password. One can manage funds in the cryptocurrency wallet by knowing the private key.
Nodes – individual computers that maintain and uphold the network’s functionality – are the custodians of decentralization, ensuring that no single entity can monopolize control over the network. Each node holds an identical copy of the blockchain and operates under a consensus mechanism to validate transactions, embodying the ethos of equality and autonomy that Bitcoin champions.
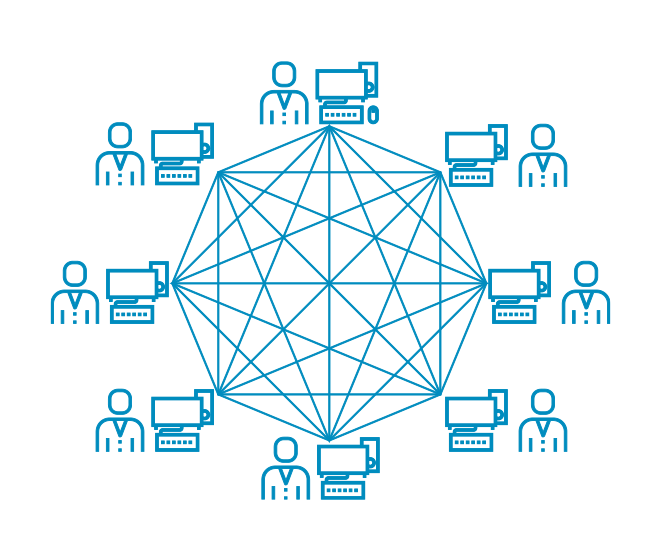
Bitcoin Network
The innovative Bitcoin network is not static but continually evolving, driven by an active community of developers, miners, and users. This dynamic interplay of technology and community underscores Bitcoin’s resilience and its potential to redefine financial paradigms.
In essence, the Bitcoin network is more than a technological marvel; it’s a socio-economic experiment on a global scale, challenging conventional notions of currency, ownership, and trust. As it matures, it continues to spark a discourse on the future of money, digital privacy, and the role of decentralized networks in a connected world, marking a significant leap toward a more inclusive and transparent financial system.
What Is Bitcoin Mining? The Concept of Proof of Work
Dubbed digital gold, Bitcoin shares a notable parallel with the physical process of mining precious minerals. In the digital realm, Bitcoin mining refers to the intricate process of generating new BTC by adding blocks to the blockchain network, a concept that Bitcoin pioneered.

The Process of Mining
At the heart of Bitcoin mining lies the blockchain, a chain of data blocks intricately linked to each other through cryptographic codes, known as hashes. These hashes ensure the integrity and “unbreakability” of the blockchain’s historical data.
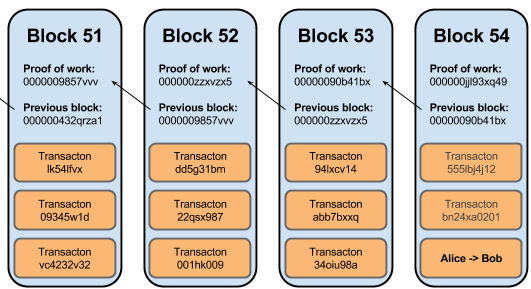
Block in a Blockchain
The mining process involves the network broadcasting a new block’s hash requirement to all active nodes. Miners, using robust hardware, compete to solve this cryptographic puzzle. The first to solve the hash validates the block and, in return, is rewarded with transaction fees and newly minted BTC. This is how a new Bitcoin is introduced into circulation.
Proof of Work (PoW) Consensus
Central to Bitcoin mining is the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism, a system that underpins the network’s security and decentralization. PoW requires miners to demonstrate computational effort, a process that consumes substantial energy but is crucial for maintaining the network’s integrity and trustworthiness. This mechanism ensures that modifying the blockchain’s history is practically impossible.
Adaptive Difficulty Adjustments
Bitcoin’s mining difficulty adjusts every 2016 blocks, or roughly every two weeks, to maintain a consistent block time of approximately 10 minutes. This dynamic adjustment ensures that as more miners join the network or as computational power increases, the difficulty of mining increases accordingly. This mechanism prevents any single miner or group from dominating the blockchain creation process, thus maintaining a decentralized and secure network.
As the network evolves, so does the complexity of mining, with the difficulty of tasks adjusting to maintain a consistent rate of block generation. This increasing difficulty necessitates more powerful and efficient mining hardware, leading to an evolving landscape where only the most efficient mining operations can sustain profitability.
While anyone with the necessary hardware can become a miner, the competitive nature of mining and the associated costs have led to the emergence of mining pools and industrial-scale mining operations.
Bitcoin Halving as Protection From Inflation
The blockchain exists because of miners, who are rewarded for each processed block. The reward size is pre-programmed in the system and is reduced every four years. This reduction in reward is the process known as “halving.”
Halving cuts the reward for mining new blocks in half, thereby reducing the rate at which new bitcoins are created and released. This event is significant as it mimics the scarcity and deflationary aspects of precious metals, contributing to Bitcoin’s value proposition as ‘digital gold.’
The halving is designed to counter inflation and prolong the mining incentive structure until all 21 million bitcoins are mined, expected around the year 2140. By reducing the supply of new bitcoins, halving events have historically been associated with notable shifts in Bitcoin’s market dynamics.
To learn more about halving, check out our article “What Is Bitcoin Halving? Everything You Need to Know“.
Decentralization as Protection From Fraud
Bitcoin’s rise as a digital asset has spotlighted its underlying security mechanisms, which are fundamental to its value and trustworthiness. Unlike traditional financial systems, Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network, relying on advanced cryptographic techniques and a consensus mechanism to maintain security and integrity.
Bitcoin Halving as Protection From Inflation
At its core, Bitcoin’s security is anchored in cryptography. Each transaction on the Bitcoin network is secured using a digital signature, which is unique and practically impossible to forge. These signatures ensure that bitcoins can only be spent by their rightful owners. Moreover, the blockchain itself, a public ledger of all Bitcoin transactions, is secured through cryptographic hashes, which are designed to be tamper-evident.
Any attempt to alter transaction data would require recalculating all subsequent blocks’ hashes, an unfeasible task given the network’s computational power. PoW secures the network and validates transactions, prevents double-spending, and ensures the network’s resistance to censorship.
Decentralization
Bitcoin’s decentralized nature is another critical aspect of its security. Instead of relying on a central point of control, Bitcoin operates across a global network of nodes. Each node possesses a complete copy of the blockchain, allowing the network to remain operational and accurate even if parts of it are compromised. This redundancy ensures that no single entity can control or manipulate the Bitcoin network.
Network Protocols and User Practices
Beyond the built-in security features, the security of Bitcoin also depends on user practices and network protocols. Users are advised to adopt secure storage methods, like hardware wallets, and to practice caution with their private keys, which are essential for accessing their bitcoins. On the network side, protocols are constantly reviewed and updated to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities, ensuring that Bitcoin adapts to the evolving landscape of digital security.
Despite its robust security features, Bitcoin is not immune to challenges. The rise of sophisticated hacking techniques and the potential for quantum computing to disrupt cryptographic standards are concerns that the community continues to address. As Bitcoin evolves, so too will its security mechanisms, adapting to new threats and incorporating advancements in cryptography and network security.
BTC: Crypto Money or Investment?
Bitcoin (BTC), as the progenitor of the cryptocurrency era, holds a pivotal place in the digital asset landscape. Its emergence as the first cryptocurrency has laid the groundwork for altcoins and continues to be the most valued and widely traded digital currency.
Market Influence and BTC Dominance
Bitcoin (BTC) is the first and largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization and trading volumes. It is traded on all known cryptocurrency exchanges, both centralized (Binance, OKX, Bybit) and decentralized (dYdX, PancakeSwap, SushiSwap).
Bitcoin dominance refers to the measure of how much of the total market capitalization (total market cap) of all cryptocurrencies is comprised of Bitcoin’s market cap. Essentially, it indicates Bitcoin’s proportion of the value in the entire cryptocurrency market. This metric is denoted as a percentage and gives you an insight into Bitcoin’s relative size and significance.
Market capitalization is the total value of a cryptocurrency and is calculated by multiplying the current price of the coin by the total number of coins in circulation. For Bitcoin, this metric reflects its economic power and liquidity within the market. When comparing Bitcoin’s market cap with that of other cryptocurrencies, you can assess its relative strength, investment health, and the potential direction of the market.
Investment and Trading
Bitcoin is one of the main trading instruments in the cryptocurrency market. New coins on cryptocurrency exchanges are typically traded primarily against Bitcoin.
Investors and traders gravitate towards Bitcoin for its pioneering status and market liquidity. The divisibility of Bitcoin surpasses that of fiat currencies, allowing microtransactions that are not feasible with traditional money.
BTC Market
However, the BTC cryptocurrency is highly volatile and can gain or lose up to 50% of its value in a relatively short time. This volatility sometimes undermines traders’ confidence. Therefore, for convenience, BTC and other cryptocurrencies are often traded in pairs with stablecoins. The CScalp team has created a free crypto screener. It allows tracking and analyzing the price dynamics of perpetual futures on Binance, Bybit, and OKX cryptocurrency exchanges. The screener simplifies the trader’s task of searching for volatile assets and helps monitor the current funding on crypto exchanges. Additionally, TradingView charts are integrated into the screener for each instrument in case you need to check a chart pattern or perform technical analysis.
Utility as a Means of Payment
Functionally, Bitcoin has all the attributes of regular money, except one: it is not represented by any physical entity in the real world and relies solely on mathematics and belief in its utility. Despite this, there have been ongoing discussions and attempts to integrate Bitcoin into existing payment systems.
Bitcoin is used (or has been used experimentally) as a means of payment by companies like Microsoft, Wikipedia, Twitch, Subway, Pizza Hut, Burger King, KFC, and others. Bitcoin is also accepted at many small businesses, online and offline stores.
Moreover, Bitcoin has set a precedent for national adoption. Under the initiative of President Nayib Bukele, El Salvador made Bitcoin its national currency in September 2021. The success of this initiative has been mixed, and the world continues to monitor the experiment’s progress. The Central African Republic became the second country to adopt Bitcoin at a national level in the spring of 2022.
What Are the Complexities of the Bitcoin Ecosystem?
Bitcoin embodies the risks and complexities inherent to digital assets. Understanding these is crucial for anyone navigating this innovative yet uncertain terrain.
Volatility and Market Risks
Despite an almost consistent global growth trend, BTC prices can experience significant fluctuations in relatively short periods, driven by market sentiment. This volatility isn’t just an intrinsic market feature; it’s shaped by a confluence of factors that extend far beyond basic supply and demand dynamics.
- Market Sentiment and Speculation: Positive news or technological advancements can lead to rapid price increases, while negative news can cause swift declines. Speculators, aiming to capitalize on price movements, can exacerbate volatility, leading to boom-and-bust cycles that challenge traditional investment strategies.
- Liquidity and Market Depth: The liquidity level, or the ability to buy or sell an asset without causing significant price changes, plays a crucial role in Bitcoin’s price stability. Limited liquidity in Bitcoin markets can lead to more pronounced price changes as large trades have a disproportionately high impact on the market price.
- Influence of Whales: Large holders of Bitcoin, often referred to as ‘whales,’ can significantly influence its price. A single large sell order can trigger price declines, initiating a cascade of sell-offs. Conversely, substantial buy orders can lead to rapid price increases, creating a self-reinforcing upward trend.
- Regulatory News and Global Events: Announcements of regulatory changes or government interventions in cryptocurrency markets can trigger significant price movements. Similarly, global economic events or financial crises can influence investors’ perception of Bitcoin as a safe haven asset, impacting its price volatility.
- Technological Changes and Adoption Rates: Innovations and updates in the Bitcoin network, like the halving events or protocol upgrades, can influence investor expectations and, subsequently, price volatility.
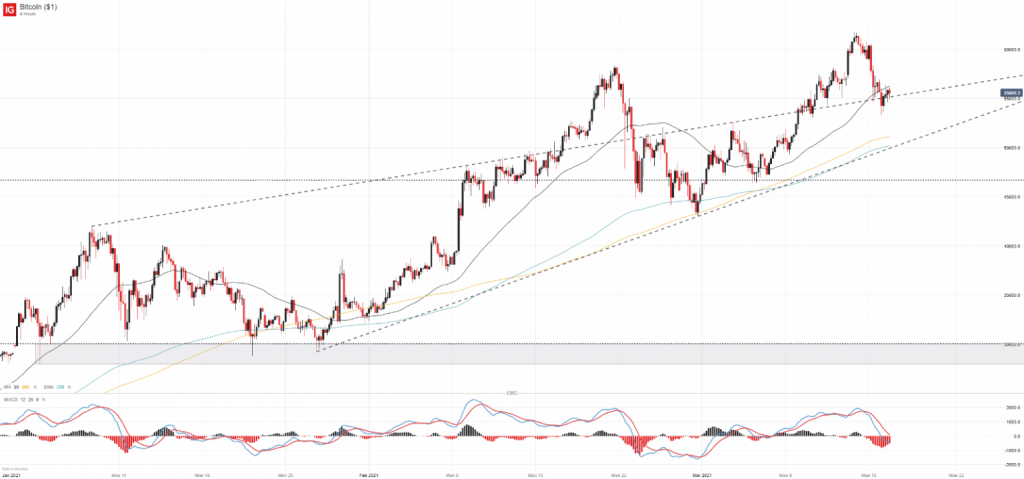
BTC Market Volatility
While volatility can present opportunities for traders and investors, it also requires a nuanced understanding of market dynamics and an acceptance of the potential for rapid and substantial value changes. For long-term investors, this volatility underscores the importance of a diversified investment strategy and a clear understanding of one’s risk tolerance when including Bitcoin in a portfolio.
Lack of Regulation
The decentralized and anonymous nature of Bitcoin is both its strength and its Achilles’ heel. While it offers freedom from traditional banking systems and governmental oversight, this very feature introduces complexities in terms of regulation and user responsibility.
In the Bitcoin network, users have complete control over their funds. This self-sovereignty brings with it the burden of security. The phrase “Not your keys, not your bitcoins” serves as a stark reminder that users who do not maintain direct control over their private keys effectively relinquish control over their Bitcoin holdings. Unlike traditional banking systems, there is no central authority to revert fraudulent transactions or recover lost funds in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Banks, governments, and financial institutions often critique Bitcoin’s lack of regulatory oversight, citing concerns about its potential misuse for illicit activities. The pseudonymous nature of Bitcoin transactions makes it a potential tool for money laundering and the financing of illegal activities.
In response to these concerns, many cryptocurrency exchanges have adopted Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures, requiring users to verify their identity. This measure aims to prevent illicit activities by making it harder for individuals to use Bitcoin for illegal purposes while maintaining an audit trail. However, this approach has sparked debate within the community, with some arguing that it undermines the privacy and freedom that cryptocurrencies were designed to offer.
The regulatory landscape for Bitcoin varies significantly across different jurisdictions, reflecting a spectrum of governmental attitudes toward cryptocurrencies. Some countries have embraced Bitcoin, recognizing it as a legitimate financial asset, while others have imposed strict regulations or outright bans. This patchwork of regulations affects how users interact with Bitcoin, influencing everything from taxation to the legality of its use.
Irreversible Transactions
One of the defining characteristics of the Bitcoin blockchain is the irreversibility of its transactions. Once a transaction is confirmed and added to the blockchain, it becomes immutable, meaning it cannot be altered or reversed.
The finality of Bitcoin transactions is a critical aspect that differentiates it from traditional financial systems, where transactions can be contested or reversed under certain circumstances, such as chargebacks or bank errors. In the Bitcoin network, once miners confirm a transaction and it is embedded in the blockchain, it is considered final. This immutability ensures that transactions are not susceptible to double-spending or fraud within the network.
When sending Bitcoin, users must double-check the recipient’s address and the amount being sent to avoid sending funds to the wrong address, falling victim to clipboard-hijacking malware that changes copied addresses, or even losing access to their wallets without recourse.
Given these risks, there is a significant emphasis within the Bitcoin community on education and the adoption of best practices. Users are encouraged to use hardware wallets for better security, to perform test transactions when transferring large amounts, and to utilize address book features in wallets to reduce the risk of address input errors. Some initiatives aim to introduce additional layers of security or recovery options, such as multi-signature transactions that require more than one key to authorize a transaction or services that provide a grace period before finalizing transactions.
Environmental Concerns
Bitcoin’s reliance on the proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism, while providing robust security and decentralization, is intrinsically linked to high energy consumption. This has sparked an ongoing debate about the environmental sustainability of Bitcoin mining, especially as the network scales and the demand for mining power increases.
The carbon footprint of Bitcoin mining is contingent on the energy sources used; the environmental implications are particularly concerning in regions where fossil fuels dominate the energy mix.
In response to these concerns, there is a growing interest within the Bitcoin community and among blockchain technologists in exploring more sustainable consensus mechanisms. Proof-of-stake (PoS) is one such alternative that is seen as a less energy-intensive option compared to PoW. PoS does not require the same computational work and, consequently, uses considerably less energy. However, transitioning Bitcoin from PoW to PoS presents significant technical and philosophical challenges, given that PoW is integral to Bitcoin’s design and perceived security model.
There is an increasing push to power Bitcoin mining operations with renewable energy sources. By transitioning to solar, wind, or hydroelectric power, the environmental impact of Bitcoin mining can be mitigated. Some mining operations are situating themselves near renewable energy sources to take advantage of lower costs and reduced carbon footprints. Additionally, there are initiatives to use the excess heat generated from mining to provide heating solutions, thereby improving energy efficiency. Some jurisdictions have started to impose regulations on mining operations, pushing them towards greater energy efficiency and sustainability.
Security Risks
Cryptocurrency exchanges, while providing a crucial service in the Bitcoin ecosystem, have been targets for high-profile hacks. These platforms, holding large amounts of digital assets, present lucrative targets for cybercriminals. Despite improved security measures over the years, the risk of exchange breaches remains, underscoring the importance of users being cautious about where and how they store their Bitcoin.
The security of a Bitcoin wallet hinges on how well the private keys are safeguarded. Wallet vulnerabilities, whether in software or hardware wallets, can expose users to theft and loss. Software wallets can be compromised by malware or phishing attacks, while hardware wallets might have vulnerabilities in their physical design or firmware. Regular updates, vigilance, and choosing reputable wallets are crucial for minimizing these risks.
The anonymity and irreversibility of Bitcoin transactions make them particularly appealing for scammers. Phishing attacks, where users are tricked into revealing their private keys or sending funds to malicious actors, are common. Education on recognizing such scams and secure browsing practices are vital defenses against these tactics.
Beyond technical exploits, social engineering remains a significant threat. Attackers often use manipulation tactics to trick individuals or employees within organizations into making security mistakes or revealing sensitive information. Awareness and training on social engineering tactics are key to safeguarding against these types of attacks.
Future Landscape of Digital Currencies: What Is Next?
As Bitcoin continues to evolve, its journey from an obscure digital token to a significant player in the financial markets is nothing short of extraordinary. However, the road ahead is fraught with both unprecedented opportunities and significant challenges.
Technological Advancements
- Lightning Network and Scalability: One of the most anticipated technological advancements for Bitcoin is the Lightning Network. This second-layer protocol aims to solve Bitcoin’s scalability issues by enabling faster and cheaper transactions. It allows for the creation of a network of micropayment channels without the need to trust intermediaries. As this network grows, it could significantly increase Bitcoin’s transaction capacity, making it more viable for everyday transactions.
- Privacy Enhancements: Bitcoin’s transparency is a double-edged sword. While it ensures security and trust, it also exposes transaction details to public scrutiny. Upcoming advancements like Schnorr Signatures and Taproot are set to enhance Bitcoin’s privacy features, making transactions more efficient and harder to trace.
- Smart Contracts: The integration of smart contracts into the Bitcoin network could redefine its capabilities. Although Bitcoin’s scripting language is not as versatile as Ethereum’s, improvements are being made to enable more complex contract functionalities. This could open up new use cases for Bitcoin, extending its utility beyond mere currency or store of value.
Adoption Trends
The increasing interest of institutional investors in Bitcoin is a bullish sign for its future. As more corporations add Bitcoin to their balance sheets and investment portfolios, it gains legitimacy and stability. However, this trend also raises concerns about market concentration and the influence of large players.
For Bitcoin to truly succeed as a currency, it needs widespread adoption at the retail level. While there are barriers to this, such as volatility and regulatory uncertainties, improvements in user experience and education could encourage more consumers and businesses to use Bitcoin for everyday transactions.
Regulatory Landscape
The future of Bitcoin will be heavily influenced by how global regulatory frameworks evolve, particularly concerning anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) policies. As Bitcoin becomes more mainstream, issues surrounding taxation and compliance come to the forefront.
What Is Bitcoin? – Conclusion
Bitcoin stands as a pioneering force in the cryptocurrency landscape, setting the benchmark and influencing the trajectory of the entire market. This groundbreaking digital currency was born with the vision of revolutionizing the financial world, offering an alternative system where ownership and management of funds are democratized, free from traditional institutional oversight.
The essence of Bitcoin extends beyond its role as a digital currency; it embodies a financial and technological innovation that challenges conventional paradigms of money exchange. By leveraging blockchain technology, Bitcoin ensures transparency and security, though it simultaneously places a significant onus of responsibility on its users. This decentralized nature underscores the critical balance between freedom and risk, empowering users while reminding them of their duties in safeguarding their digital assets.
In conclusion, Bitcoin is not just a cryptocurrency; it’s a movement that advocates for a shift in how we perceive and interact with money. As we move deeper into the digital era, Bitcoin’s journey offers valuable insights into the evolving relationship between technology, society, and financial autonomy, marking a significant chapter in the annals of economic history.
Frequently Asked Questions: FAQs About “What Is Bitcoin?”
What Is Blockchain?
Most cryptocurrencies run on a distributed public ledger called blockchain. Blockchains are best known for their crucial role in cryptocurrency systems, such as Bitcoin, for maintaining a secure and decentralized record of transactions. Each transaction is verified by consensus among participants in the network, making fraud and double-spending nearly impossible.
What Does Bitcoin Network Do?
Bitcoin is a form of digital currency that uses blockchain technology to support transactions between users. This network is maintained by nodes (computers) that validate and record transactions, operating on a peer to peer basis. The Bitcoin network facilitates a range of functions crucial to the operation of Bitcoin as a decentralized digital currency. Here’s what it does: transaction processing, maintaining the ledger (blockchain), consensus building, currency issuance: security and verification.
What Is Bitcoin Mining?
Bitcoin mining is the process of adding new blocks to the Bitcoin blockchain. Miners compete to solve complex cryptographic puzzles using hardware power, and the first to solve it validates the block, receiving Bitcoin as a reward.
How Is Bitcoin Used?
While Bitcoin can be used for transactions where accepted, it is predominantly used as a means for investment and trading, similar to gold, serving as a store of value and a medium for capital transfer.
What Are the Risks Associated With Bitcoin Cryptocurrency?
Bitcoin is known for its price volatility and lack of regulation, which can lead to significant price fluctuations and risks such as loss of funds and fraud. Additionally, its transactions are
irreversible.
Can Bitcoin Be Regulated?
An innovative payment network and a digital currency, Bitcoin is a decentralized digital asset and a form of digital currency that aims to eliminate the need for central authorities. While the activities of Bitcoin users can be subject to regulations within specific jurisdictions, the decentralized nature of Bitcoin itself makes it inherently resistant to centralized regulatory control.
How Does Bitcoin Maintain User Privacy?
Bitcoin is digital money that allows for secure peer to peer transactions on the Internet without the need for intermediaries such as banks or payment processors. Bitcoin transactions do not collect personal user data but operate using a system of public and private cryptographic keys. These keys enable transactions while maintaining user anonymity.
What Is the Significance of Bitcoin’s Market Dominance?
Bitcoin’s definitely the name of the best known cryptocurrency. It holds the biggest crypto market share. Its market dominance, illustrated by the Bitcoin Dominance Index, shows how much of the total cryptocurrency market capitalization is comprised of Bitcoin. It’s a measure of Bitcoin’s influence and standing in the cryptocurrency market.
Join the CScalp Trading Community
Join our official trader's chat. Here you can communicate with other scalpers, find trading soulmates and discuss the market. We also have an exclusive chat for crypto traders!
Don't forget to subscribe to our official CScalp news channel, use trading signals and get to know our bot.
If you have any questions, just contact our platform's support via Telegram at @CScalp_support_bot. We will respond in a matter of seconds.
You can also visit our Discord channel and subscribe to the CScalp TV YouTube channel.
JOIN OUR CHAT
